Page 276 -
P. 276
234 Chapter 8 • Program and Project Management
processes that will be included in the implementation based on the projects goals. These goals have
a direct effect on which software modules will be implemented and the number of business units that
will participate in this implementation. Scope creep is defined as constant changes to the parameters
outlined in the original project goals. It was stated earlier that one of the roles of project management
is to make sure the project meets its goals in relation to cost, quality, and time. Scope creep has a
detrimental effect on meeting this objective. To prevent scope creep, the project manager must
ensure that the parameters of the project are outlined in the business case, a project charter, or a
mission statement. There is always some change in scope as a project progresses, but the project
manager must make sure to have a formal process in place in order to manage that change effort. It
is not unusual for organizations to implement a change control board, which includes users and
senior management to address these instances.
Teamwork
The teamwork concept cannot be emphasized enough (Table 8-1). In most ERP implementations,
project teams are assembled by bringing together staff from the existing organization, new hires, and
possible external consultants. Teamwork does not just happen without some effort in training and
team building. Each team will have its own set of dynamics based on the knowledge and personali-
ties of the people involved. It takes savvy project managers and project leads to develop and build
teams to address the many issues that will confront the teams as the project moves forward. If team-
work is not incorporated into a project, it will be much more difficult to keep on track, and it will
likely cost more in resources.
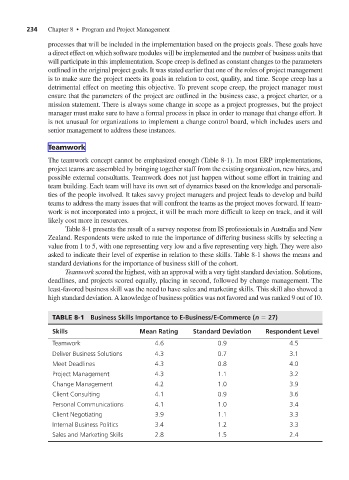
Table 8-1 presents the result of a survey response from IS professionals in Australia and New
Zealand. Respondents were asked to rate the importance of differing business skills by selecting a
value from 1 to 5, with one representing very low and a five representing very high. They were also
asked to indicate their level of expertise in relation to these skills. Table 8-1 shows the means and
standard deviations for the importance of business skill of the cohort.
Teamwork scored the highest, with an approval with a very tight standard deviation. Solutions,
deadlines, and projects scored equally, placing in second, followed by change management. The
least-favored business skill was the need to have sales and marketing skills. This skill also showed a
high standard deviation. A knowledge of business politics was not favored and was ranked 9 out of 10.
TABLE 8-1 Business Skills Importance to E-Business/E-Commerce (n = 27)
Skills Mean Rating Standard Deviation Respondent Level
Teamwork 4.6 0.9 4.5
Deliver Business Solutions 4.3 0.7 3.1
Meet Deadlines 4.3 0.8 4.0
Project Management 4.3 1.1 3.2
Change Management 4.2 1.0 3.9
Client Consulting 4.1 0.9 3.6
Personal Communications 4.1 1.0 3.4
Client Negotiating 3.9 1.1 3.3
Internal Business Politics 3.4 1.2 3.3
Sales and Marketing Skills 2.8 1.5 2.4