Page 333 -
P. 333
Chapter 10 • Global, Ethics, and Security Management 291
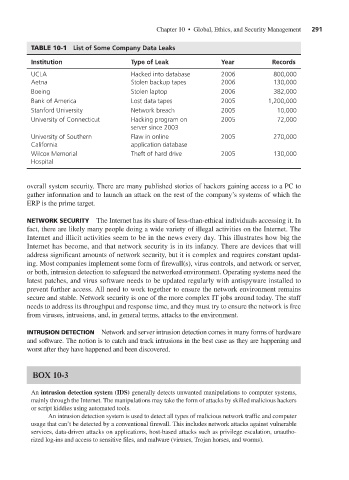
TABLE 10-1 List of Some Company Data Leaks
Institution Type of Leak Year Records
UCLA Hacked into database 2006 800,000
Aetna Stolen backup tapes 2006 130,000
Boeing Stolen laptop 2006 382,000
Bank of America Lost data tapes 2005 1,200,000
Stanford University Network breach 2005 10,000
University of Connecticut Hacking program on 2005 72,000
server since 2003
University of Southern Flaw in online 2005 270,000
California application database
Wilcox Memorial Theft of hard drive 2005 130,000
Hospital
overall system security. There are many published stories of hackers gaining access to a PC to
gather information and to launch an attack on the rest of the company’s systems of which the
ERP is the prime target.
NETWORK SECURITY The Internet has its share of less-than-ethical individuals accessing it. In
fact, there are likely many people doing a wide variety of illegal activities on the Internet. The
Internet and illicit activities seem to be in the news every day. This illustrates how big the
Internet has become, and that network security is in its infancy. There are devices that will
address significant amounts of network security, but it is complex and requires constant updat-
ing. Most companies implement some form of firewall(s), virus controls, and network or server,
or both, intrusion detection to safeguard the networked environment. Operating systems need the
latest patches, and virus software needs to be updated regularly with antispyware installed to
prevent further access. All need to work together to ensure the network environment remains
secure and stable. Network security is one of the more complex IT jobs around today. The staff
needs to address its throughput and response time, and they must try to ensure the network is free
from viruses, intrusions, and, in general terms, attacks to the environment.
INTRUSION DETECTION Network and server intrusion detection comes in many forms of hardware
and software. The notion is to catch and track intrusions in the best case as they are happening and
worst after they have happened and been discovered.
BOX 10-3
An intrusion detection system (IDS) generally detects unwanted manipulations to computer systems,
mainly through the Internet. The manipulations may take the form of attacks by skilled malicious hackers
or script kiddies using automated tools.
An intrusion detection system is used to detect all types of malicious network traffic and computer
usage that can’t be detected by a conventional firewall. This includes network attacks against vulnerable
services, data-driven attacks on applications, host-based attacks such as privilege escalation, unautho-
rized log-ins and access to sensitive files, and malware (viruses, Trojan horses, and worms).