Page 43 - Environmental Control in Petroleum Engineering
P. 43
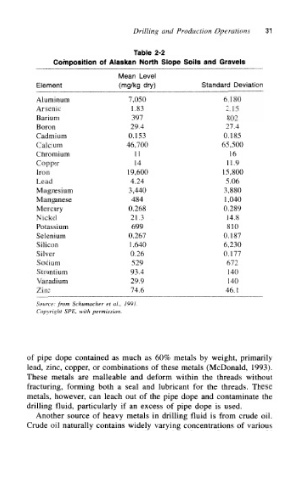
Drilling and Production Operations 31
Table 2-2
Composition of Alaskan North Slope Soils and Gravels
Mean Level
Element {mg/kg dry) Standard Deviation
Aluminum 7,050 6,180
Arsenic 1.83 2.15
Barium 397 802
Boron 29.4 27,4
Cadmium 0.153 0,185
Calcium 46,700 65,500
Chromium 11 16
Copper 14 11.9
Iron 19,600 15,800
Lead 4.24 5.06
Magnesium 3,440 3,880
Manganese 484 1,040
Mercury 0.268 0.289
Nickel 21.3 14.8
Potassium 699 810
Selenium 0.267 0.187
Silicon 1,640 6,230
Silver 0.26 0.177
Sodium 529 672
Strontium 93.4 140
Vanadium 29.9 140
Zinc 74.6 46.1
Source: from Schumacher et al, 1991.
Copyright SPE, with permission.
of pipe dope contained as much as 60% metals by weight, primarily
lead, zinc, copper, or combinations of these metals (McDonald, 1993).
These metals are malleable and deform within the threads without
fracturing, forming both a seal and lubricant for the threads. These
metals, however, can leach out of the pipe dope and contaminate the
drilling fluid, particularly if an excess of pipe dope is used.
Another source of heavy metals in drilling fluid is from crude oil.
Crude oil naturally contains widely varying concentrations of various