Page 110 - Environmental Nanotechnology Applications and Impacts of Nanomaterials
P. 110
96 Principles and Methods
The addition of oxygen moieties to SWNT sidewalls can be achieved
by treatment with acid or wet air oxidation and ozonolysis [206]. The
direct epoxidation of SWNTs may be accomplished by the reaction with
either trifluorodimethyldioxirane, formed in situ from trifluoroacetone
4
and Oxone (potassium peroxymonosulfate, KHSO ) in MeCN/H O or
5
2
3-chloroperoxybenzoic acid (m-CPBA)/CH Cl [207], or using ReMeO /H O 2
3
2
2
2
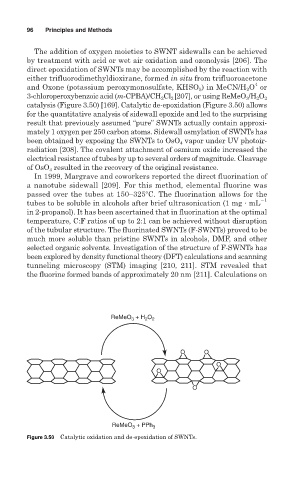
catalysis (Figure 3.50) [169]. Catalytic de-epoxidation (Figure 3.50) allows
for the quantitative analysis of sidewall epoxide and led to the surprising
result that previously assumed “pure” SWNTs actually contain approxi-
mately 1 oxygen per 250 carbon atoms. Sidewall osmylation of SWNTs has
been obtained by exposing the SWNTs to OsO vapor under UV photoir-
4
radiation [208]. The covalent attachment of osmium oxide increased the
electrical resistance of tubes by up to several orders of magnitude. Cleavage
of OsO resulted in the recovery of the original resistance.
4
In 1999, Margrave and coworkers reported the direct fluorination of
a nanotube sidewall [209]. For this method, elemental fluorine was
passed over the tubes at 150–325 C. The fluorination allows for the
1
tubes to be soluble in alcohols after brief ultrasonication (1 mg mL
in 2-propanol). It has been ascertained that in fluorination at the optimal
temperature, C:F ratios of up to 2:1 can be achieved without disruption
of the tubular structure. The fluorinated SWNTs (F-SWNTs) proved to be
much more soluble than pristine SWNTs in alcohols, DMF, and other
selected organic solvents. Investigation of the structure of F-SWNTs has
been explored by density functional theory (DFT) calculations and scanning
tunneling microscopy (STM) imaging [210, 211]. STM revealed that
the fluorine formed bands of approximately 20 nm [211]. Calculations on
ReMeO + H O 2
2
3
O O
O
O
O
ReMeO 3 + PPh 3
Figure 3.50 Catalytic oxidation and de-epoxidation of SWNTs.