Page 353 - Environmental Nanotechnology Applications and Impacts of Nanomaterials
P. 353
338 Environmental Applications of Nanomaterials
innovations in membrane processes used to protect our environment and
public health. We then examine several examples of nanomaterial-based
approaches to improved membrane technologies.
Overview of Membrane Processes
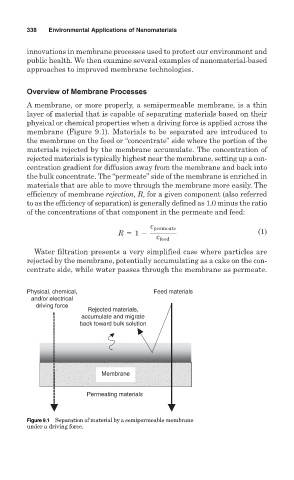
A membrane, or more properly, a semipermeable membrane, is a thin
layer of material that is capable of separating materials based on their
physical or chemical properties when a driving force is applied across the
membrane (Figure 9.1). Materials to be separated are introduced to
the membrane on the feed or “concentrate” side where the portion of the
materials rejected by the membrane accumulate. The concentration of
rejected materials is typically highest near the membrane, setting up a con-
centration gradient for diffusion away from the membrane and back into
the bulk concentrate. The “permeate” side of the membrane is enriched in
materials that are able to move through the membrane more easily. The
efficiency of membrane rejection, R, for a given component (also referred
to as the efficiency of separation) is generally defined as 1.0 minus the ratio
of the concentrations of that component in the permeate and feed:
c permeate
R 5 1 2 (1)
c feed
Water filtration presents a very simplified case where particles are
rejected by the membrane, potentially accumulating as a cake on the con-
centrate side, while water passes through the membrane as permeate.
Physical, chemical, Feed materials
and/or electrical
driving force
Rejected materials,
accumulate and migrate
back toward bulk solution
Membrane
Permeating materials
Figure 9.1 Separation of material by a semipermeable membrane
under a driving force.