Page 425 - Environmental Nanotechnology Applications and Impacts of Nanomaterials
P. 425
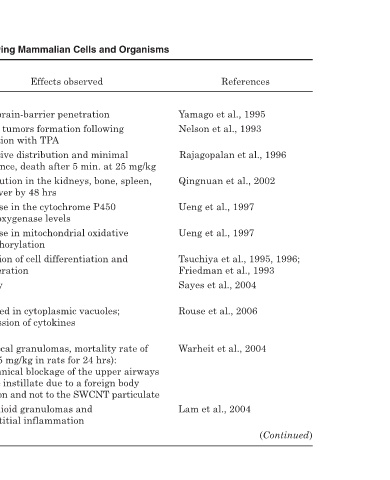
References Yamago et al., 1995 Nelson et al., 1993 Rajagopalan et al., 1996 Qingnuan et al., 2002 Ueng et al., 1997 Ueng et al., 1997 Tsuchiya et al., 1995, 1996; Friedman et al., 1993 Sayes et al., 2004 Rouse et al., 2006 Warheit et al., 2004 Lam et al., 2004 (Continued)
Negative Impacts of Carbon-Based Nanomaterials on Living Mammalian Cells and Organisms
Effects observed Blood-brain-barrier penetration Benign tumors formation following initiation with TPA Extensive distribution and minimal clearance, death after 5 min. at 25 mg/kg Distribution in the kidneys, bone, spleen, and liver by 48 hrs Decrease in the cytochrome P450 monooxygenase level
Organisms, or cell types, or organelles Rat (IV administration) Mouse (skin applications) Rat (intravenous administration) Mice and rabbits Mice Liver microsomes Mouse midbrain cell differentiation system Human carcinoma cells and dermal fibroblasts Human epidermal keratinocytes Rat lung
TABLE 11.1 Type of nanomaterials Fullerene water suspension C 60 MSAD-C 60 C 60 (OH) x Fullerenol-1 C 60 -PVP Colloidal and derivatized C 60 Functionalized fullerenes SWCNT Underivatized SWCNT
407