Page 201 - Excel Data Analysis
P. 201
10 537547 Ch09.qxd 3/4/03 12:13 PM Page 187
AUTOMATING ACTIONS WITH MACROS 9
You can use named arguments to simplify your function calls.
When you work with built-in VBA functions, you see that many of
the functions have optional arguments. For example, although the
InputBox has seven different arguments, only the first one is
required. If you want to specify any additional arguments, you
must specify the argument values in order, leaving a placeholder
for any that you do not want to use.
Example:
UserInput = InputBox("Type a value", , "test")
Instead of specifying a placeholder for each value, VBA also
enables you to use named arguments with the built-in
procedures. When you use a named argument, you specify the
name of the argument along with the corresponding value. To
specify a named argument, you type the name of the argument
followed by a colon, an equals sign, and the value of that
particular argument. You can specify named arguments in any
order, and you do not have to specify a value for every argument.
Example:
UserInput = InputBox(prompt:="Type a value.", default:="5")
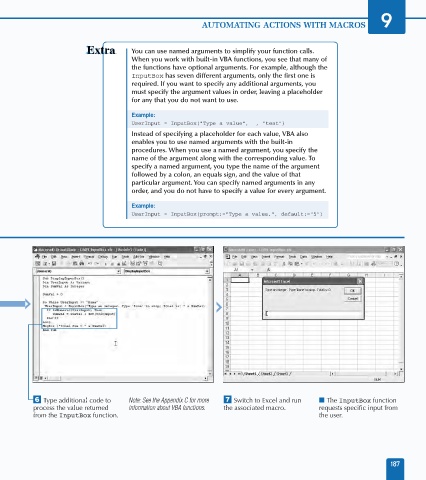
Á Type additional code to Note: See the Appendix C for more ‡ Switch to Excel and run ■ The InputBox function
process the value returned information about VBA functions. the associated macro. requests specific input from
from the InputBox function. the user.
187