Page 287 - Excel Data Analysis
P. 287
16 537547 AppD.qxd 3/4/03 11:55 AM Page 273
FORMULA BASICS IN EXCEL D
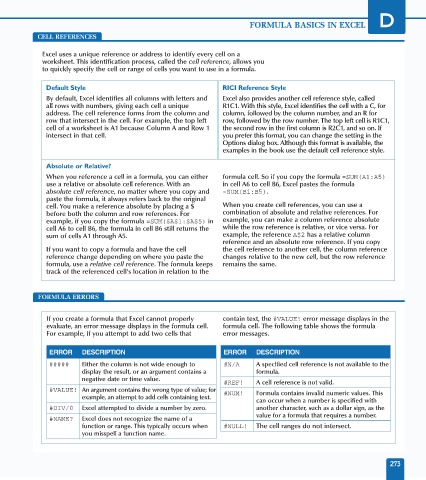
CELL REFERENCES
Excel uses a unique reference or address to identify every cell on a
worksheet. This identification process, called the cell reference, allows you
to quickly specify the cell or range of cells you want to use in a formula.
Default Style RICI Reference Style
By default, Excel identifies all columns with letters and Excel also provides another cell reference style, called
all rows with numbers, giving each cell a unique R1C1. With this style, Excel identifies the cell with a C, for
address. The cell reference forms from the column and column, followed by the column number, and an R for
row that intersect in the cell. For example, the top left row, followed by the row number. The top left cell is R1C1,
cell of a worksheet is A1 because Column A and Row 1 the second row in the first column is R2C1, and so on. If
intersect in that cell. you prefer this format, you can change the setting in the
Options dialog box. Although this format is available, the
examples in the book use the default cell reference style.
Absolute or Relative?
When you reference a cell in a formula, you can either formula cell. So if you copy the formula =SUM(A1:A5)
use a relative or absolute cell reference. With an in cell A6 to cell B6, Excel pastes the formula
absolute cell reference, no matter where you copy and =SUM(B1:B5).
paste the formula, it always refers back to the original
cell. You make a reference absolute by placing a $ When you create cell references, you can use a
before both the column and row references. For combination of absolute and relative references. For
example, if you copy the formula =SUM($A$1:$A$5) in example, you can make a column reference absolute
cell A6 to cell B6, the formula in cell B6 still returns the while the row reference is relative, or vice versa. For
sum of cells A1 through A5. example, the reference A$2 has a relative column
reference and an absolute row reference. If you copy
If you want to copy a formula and have the cell the cell reference to another cell, the column reference
reference change depending on where you paste the changes relative to the new cell, but the row reference
formula, use a relative cell reference. The formula keeps remains the same.
track of the referenced cell's location in relation to the
FORMULA ERRORS
If you create a formula that Excel cannot properly contain text, the #VALUE! error message displays in the
evaluate, an error message displays in the formula cell. formula cell. The following table shows the formula
For example, if you attempt to add two cells that error messages.
ERROR DESCRIPTION ERROR DESCRIPTION
##### Either the column is not wide enough to #N/A A specified cell reference is not available to the
display the result, or an argument contains a formula.
negative date or time value.
#REF! A cell reference is not valid.
#VALUE! An argument contains the wrong type of value; for #NUM! Formula contains invalid numeric values. This
example, an attempt to add cells containing text.
can occur when a number is specified with
#DIV/0 Excel attempted to divide a number by zero. another character, such as a dollar sign, as the
value for a formula that requires a number.
#NAME? Excel does not recognize the name of a
function or range. This typically occurs when #NULL! The cell ranges do not intersect.
you misspell a function name.
273