Page 97 - Excel Progamming Weekend Crash Course
P. 97
h540629 ch05.qxd 9/2/03 9:33 AM Page 72
72 Saturday Morning
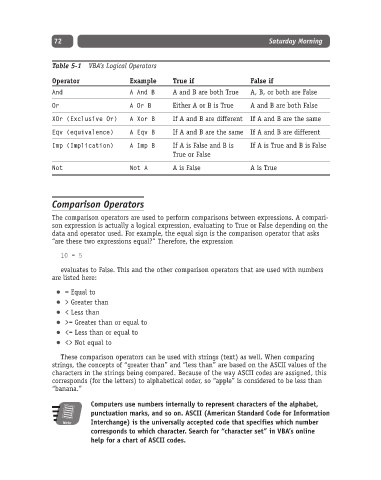
Table 5-1 VBA’s Logical Operators
Operator Example True if False if
And A And B A and B are both True A, B, or both are False
Or A Or B Either A or B is True A and B are both False
XOr (Exclusive Or) A Xor B If A and B are different If A and B are the same
Eqv (equivalence) A Eqv B If A and B are the same If A and B are different
Imp (Implication) A Imp B If A is False and B is If A is True and B is False
True or False
Not Not A A is False A is True
Comparison Operators
The comparison operators are used to perform comparisons between expressions. A compari-
son expression is actually a logical expression, evaluating to True or False depending on the
data and operator used. For example, the equal sign is the comparison operator that asks
“are these two expressions equal?” Therefore, the expression
10 = 5
evaluates to False. This and the other comparison operators that are used with numbers
are listed here:
= Equal to
> Greater than
< Less than
>= Greater than or equal to
<= Less than or equal to
<> Not equal to
These comparison operators can be used with strings (text) as well. When comparing
strings, the concepts of “greater than” and “less than” are based on the ASCII values of the
characters in the strings being compared. Because of the way ASCII codes are assigned, this
corresponds (for the letters) to alphabetical order, so “apple” is considered to be less than
“banana.”
Computers use numbers internally to represent characters of the alphabet,
punctuation marks, and so on. ASCII (American Standard Code for Information
Note Interchange) is the universally accepted code that specifies which number
corresponds to which character. Search for “character set” in VBA’s online
help for a chart of ASCII codes.