Page 339 - Failure Analysis Case Studies II
P. 339
324
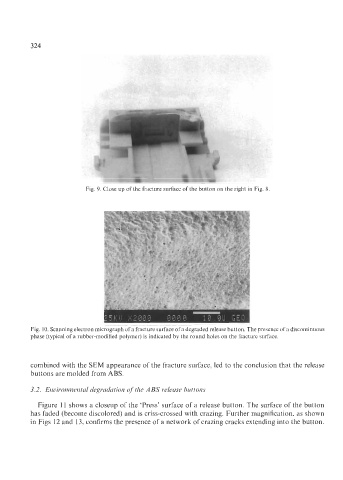
Fig. 9. Close up of the fracture surface of the button on the right in Fig. 8
Fig. 10. Scanning electron micrograph of a fracture surface of a degraded release button. The presence of a discontinuous
phase (typical of a rubber-modified polymer) is indicated by the round holes on the fracture surface.
combined with the SEM appearance of the fracture surface, led to the conclusion that the release
buttons are molded from ABS.
3.2, Environmental degradation of the ABS release buttons
Figure 11 shows a closeup of the 'Press' surface of a release button. The surface of the button
has faded (become discolored) and is criss-crossed with crazing. Further magnification, as shown
in Figs 12 and 13, confirms the presence of a network of crazing cracks extending into the button.