Page 69 - Fair, Geyer, and Okun's Water and wastewater engineering : water supply and wastewater removal
P. 69
JWCL344_ch02_029-060.qxd 8/2/10 9:14 PM Page 32
32 Chapter 2 Water Sources: Surface Water
Intake crib,
tower, or
gatehouse Pumping station
Vertical
Footbridge pump
To
treatment plant
Inlets
Intake pipe or tunnel
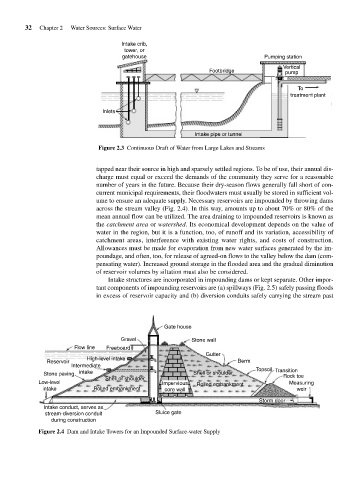
Figure 2.3 Continuous Draft of Water from Large Lakes and Streams
tapped near their source in high and sparsely settled regions. To be of use, their annual dis-
charge must equal or exceed the demands of the community they serve for a reasonable
number of years in the future. Because their dry-season flows generally fall short of con-
current municipal requirements, their floodwaters must usually be stored in sufficient vol-
ume to ensure an adequate supply. Necessary reservoirs are impounded by throwing dams
across the stream valley (Fig. 2.4). In this way, amounts up to about 70% or 80% of the
mean annual flow can be utilized. The area draining to impounded reservoirs is known as
the catchment area or watershed. Its economical development depends on the value of
water in the region, but it is a function, too, of runoff and its variation, accessibility of
catchment areas, interference with existing water rights, and costs of construction.
Allowances must be made for evaporation from new water surfaces generated by the im-
poundage, and often, too, for release of agreed-on flows to the valley below the dam (com-
pensating water). Increased ground storage in the flooded area and the gradual diminution
of reservoir volumes by siltation must also be considered.
Intake structures are incorporated in impounding dams or kept separate. Other impor-
tant components of impounding reservoirs are (a) spillways (Fig. 2.5) safely passing floods
in excess of reservoir capacity and (b) diversion conduits safely carrying the stream past
Gate house
Gravel Stone wall
Flow line Freeboard
Gutter
High-level intake
Reservoir Berm
Intermediate
Stone paving intake Shell or shoulder Topsoil Transition
Rock toe
Shell or shoulder
Low-level Impervious Rolled embankment Measuring
intake Rolled embankment core wall weir
Storm door
Intake conduct, serves as
stream-diversion conduit Sluice gate
during construction
Figure 2.4 Dam and Intake Towers for an Impounded Surface-water Supply