Page 76 - Fair, Geyer, and Okun's Water and wastewater engineering : water supply and wastewater removal
P. 76
JWCL344_ch02_029-060.qxd 8/2/10 9:14 PM Page 39
2.5 Loss by Evaporation, Seepage, and Silting 39
99.9 0.1
146 MG once in 100 years 1 5
137 MG once in 50 years
Percent of years in which required storage was equal to or less than stated magnitude 90 10 Percent of years in which required storage was equal to or greater than stated magnitude
99
123 MG once in 20 years
95
20
80
70
30
40
60
50
50
60
40
70
30
20
80
10
95
99
1 5 Straight line of best fit 90
0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160
Storage, MG
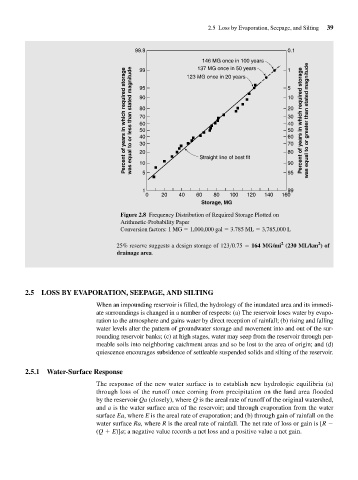
Figure 2.8 Frequency Distribution of Required Storage Plotted on
Arithmetic-Probability Paper
Conversion factors: 1 MG 1,000,000 gal 3.785 ML 3,785,000 L
2
2
25% reserve suggests a design storage of 123>0.75 164 MG/mi (230 ML/km ) of
drainage area.
2.5 LOSS BY EVAPORATION, SEEPAGE, AND SILTING
When an impounding reservoir is filled, the hydrology of the inundated area and its immedi-
ate surroundings is changed in a number of respects: (a) The reservoir loses water by evapo-
ration to the atmosphere and gains water by direct reception of rainfall; (b) rising and falling
water levels alter the pattern of groundwater storage and movement into and out of the sur-
rounding reservoir banks; (c) at high stages, water may seep from the reservoir through per-
meable soils into neighboring catchment areas and so be lost to the area of origin; and (d)
quiescence encourages subsidence of settleable suspended solids and silting of the reservoir.
2.5.1 Water-Surface Response
The response of the new water surface is to establish new hydrologic equilibria (a)
through loss of the runoff once coming from precipitation on the land area flooded
by the reservoir Qa (closely), where Q is the areal rate of runoff of the original watershed,
and a is the water surface area of the reservoir; and through evaporation from the water
surface Ea, where E is the areal rate of evaporation; and (b) through gain of rainfall on the
water surface Ra, where R is the areal rate of rainfall. The net rate of loss or gain is [R
(Q E)]a; a negative value records a net loss and a positive value a net gain.