Page 79 - Fiber Fracture
P. 79
64 J.W.S. Hearle
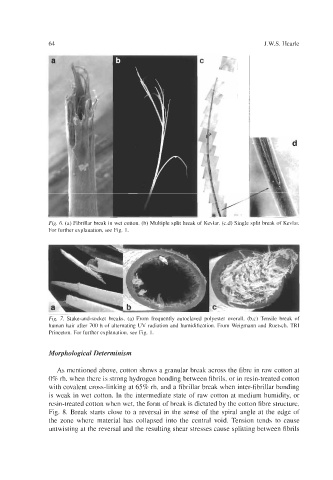
Fig. 6. (a) Fibrillar break in wet cotton. (b) Multiple split break of Kevlar. (c,d) Single split break of Kevlar.
For further explanation, see Fig. 1.
Fig. 7. Stake-and-socket breaks. (a) From frequently autoclaved polyester overall. (b,c) Tensile break of
human hair after 700 h of alternating UV radiation and humidification. From Weigmann and Ruetsch, TRI
Princeton. For further explanation, see Fig. 1.
Morphological Determinism
As mentioned above, cotton shows a granular break across the fibre in raw cotton at
0% rh, when there is strong hydrogen bonding between fibrils, or in resin-treated cotton
with covalent cross-linking at 65% rh, and a fibrillar break when inter-fibrillar bonding
is weak in wet cotton. In the intermediate state of raw cotton at medium humidity, or
resin-treated cotton when wet, the form of break is dictated by the cotton fibre structure,
Fig. 8. Break starts close to a reversal in the sense of the spiral angle at the edge of
the zone where material has collapsed into the central void. Tension tends to cause
untwisting at the reversal and the resulting shear stresses cause splitting between fibrils