Page 363 - Flexible Robotics in Medicine
P. 363
Electromechanical characterization of magnetic responsive and conductive 355
3000
2500
Conductivity (S/cm) 1500
2000
1000
500
0
0 1 2 3 4 5
Ratio of PEDOT:PSS to Fe 3 O 4 (1:x)
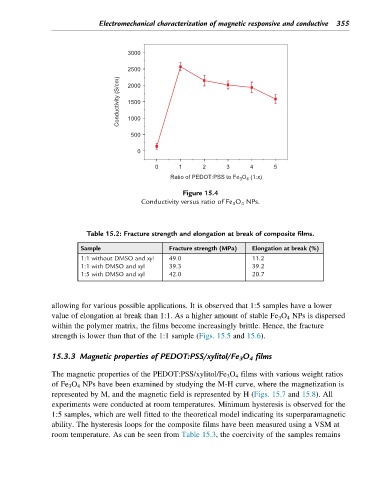
Figure 15.4
Conductivity versus ratio of Fe 3 O 4 NPs.
Table 15.2: Fracture strength and elongation at break of composite films.
Sample Fracture strength (MPa) Elongation at break (%)
1:1 without DMSO and xyl 49.0 11.2
1:1 with DMSO and xyl 39.3 39.2
1:5 with DMSO and xyl 42.0 20.7
allowing for various possible applications. It is observed that 1:5 samples have a lower
value of elongation at break than 1:1. As a higher amount of stable Fe 3 O 4 NPs is dispersed
within the polymer matrix, the films become increasingly brittle. Hence, the fracture
strength is lower than that of the 1:1 sample (Figs. 15.5 and 15.6).
15.3.3 Magnetic properties of PEDOT:PSS/xylitol/Fe 3 O 4 films
The magnetic properties of the PEDOT:PSS/xylitol/Fe 3 O 4 films with various weight ratios
of Fe 3 O 4 NPs have been examined by studying the M-H curve, where the magnetization is
represented by M, and the magnetic field is represented by H (Figs. 15.7 and 15.8). All
experiments were conducted at room temperatures. Minimum hysteresis is observed for the
1:5 samples, which are well fitted to the theoretical model indicating its superparamagnetic
ability. The hysteresis loops for the composite films have been measured using a VSM at
room temperature. As can be seen from Table 15.3, the coercivity of the samples remains