Page 61 - Flexible Robotics in Medicine
P. 61
Cable-driven flexible endoscope utilizing diamond-shaped perforations: FlexDiamond 45
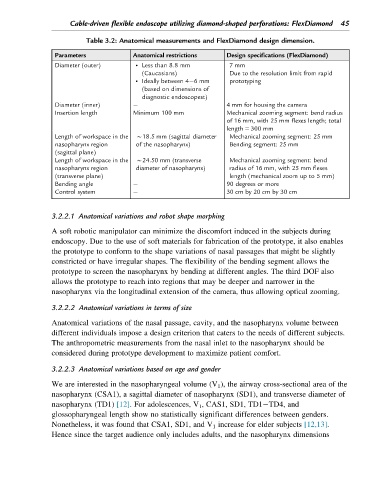
Table 3.2: Anatomical measurements and FlexDiamond design dimension.
Parameters Anatomical restrictions Design specifications (FlexDiamond)
Diameter (outer) Less than 8.8 mm 7mm
(Caucasians) Due to the resolution limit from rapid
Ideally between 4 6mm prototyping
(based on dimensions of
diagnostic endoscopest)
Diameter (inner) 4 mm for housing the camera
Insertion length Minimum 100 mm Mechanical zooming segment: bend radius
of 16 mm, with 25 mm flexes length; total
length 5 300 mm
Length of workspace in the B18.5 mm (sagittal diameter Mechanical zooming segment: 25 mm
nasopharynx region of the nasopharynx) Bending segment: 25 mm
(sagittal plane)
Length of workspace in the B24.50 mm (transverse Mechanical zooming segment: bend
nasopharynx region diameter of nasopharynx) radius of 16 mm, with 25 mm flexes
(transverse plane) length (mechanical zoom up to 5 mm)
Bending angle 90 degrees or more
Control system 30 cm by 20 cm by 30 cm
3.2.2.1 Anatomical variations and robot shape morphing
A soft robotic manipulator can minimize the discomfort induced in the subjects during
endoscopy. Due to the use of soft materials for fabrication of the prototype, it also enables
the prototype to conform to the shape variations of nasal passages that might be slightly
constricted or have irregular shapes. The flexibility of the bending segment allows the
prototype to screen the nasopharynx by bending at different angles. The third DOF also
allows the prototype to reach into regions that may be deeper and narrower in the
nasopharynx via the longitudinal extension of the camera, thus allowing optical zooming.
3.2.2.2 Anatomical variations in terms of size
Anatomical variations of the nasal passage, cavity, and the nasopharynx volume between
different individuals impose a design criterion that caters to the needs of different subjects.
The anthropometric measurements from the nasal inlet to the nasopharynx should be
considered during prototype development to maximize patient comfort.
3.2.2.3 Anatomical variations based on age and gender
We are interested in the nasopharyngeal volume (V 1 ), the airway cross-sectional area of the
nasopharynx (CSA1), a sagittal diameter of nasopharynx (SD1), and transverse diameter of
nasopharynx (TD1) [12]. For adolescences, V 1 , CAS1, SD1, TD1 TD4, and
glossopharyngeal length show no statistically significant differences between genders.
Nonetheless, it was found that CSA1, SD1, and V 1 increase for elder subjects [12,13].
Hence since the target audience only includes adults, and the nasopharynx dimensions