Page 63 - Flexible Robotics in Medicine
P. 63
Cable-driven flexible endoscope utilizing diamond-shaped perforations: FlexDiamond 47
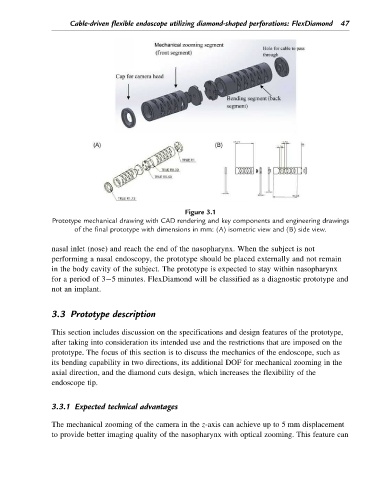
Figure 3.1
Prototype mechanical drawing with CAD rendering and key components and engineering drawings
of the final prototype with dimensions in mm: (A) isometric view and (B) side view.
nasal inlet (nose) and reach the end of the nasopharynx. When the subject is not
performing a nasal endoscopy, the prototype should be placed externally and not remain
in the body cavity of the subject. The prototype is expected to stay within nasopharynx
for a period of 3 5 minutes. FlexDiamond will be classified as a diagnostic prototype and
not an implant.
3.3 Prototype description
This section includes discussion on the specifications and design features of the prototype,
after taking into consideration its intended use and the restrictions that are imposed on the
prototype. The focus of this section is to discuss the mechanics of the endoscope, such as
its bending capability in two directions, its additional DOF for mechanical zooming in the
axial direction, and the diamond cuts design, which increases the flexibility of the
endoscope tip.
3.3.1 Expected technical advantages
The mechanical zooming of the camera in the z-axis can achieve up to 5 mm displacement
to provide better imaging quality of the nasopharynx with optical zooming. This feature can