Page 51 - Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics of Turbomachinery
P. 51
32 Fluid Mechanics, Thermodynamics of Turbomachinery
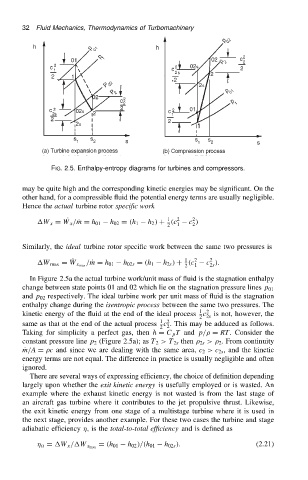
FIG. 2.5. Enthalpy-entropy diagrams for turbines and compressors.
may be quite high and the corresponding kinetic energies may be significant. On the
other hand, for a compressible fluid the potential energy terms are usually negligible.
Hence the actual turbine rotor specific work
1
2
W x D P W x / Pm D h 01 h 02 D .h 1 h 2 / C .c 2 c /
2 1 2
Similarly, the ideal turbine rotor specific work between the same two pressures is
1
2
/ Pm D h 01 h 02s D .h 1 h 2s / C .c 2 c /.
2
W max D P W x max 1 2s
In Figure 2.5a the actual turbine work/unit mass of fluid is the stagnation enthalpy
change between state points 01 and 02 which lie on the stagnation pressure lines p 01
and p 02 respectively. The ideal turbine work per unit mass of fluid is the stagnation
enthalpy change during the isentropic process between the same two pressures. The
1 2
kinetic energy of the fluid at the end of the ideal process c is not, however, the
2 2s
1 2
same as that at the end of the actual process c . This may be adduced as follows.
2 2
Taking for simplicity a perfect gas, then h D C p T and p/ D RT. Consider the
constant pressure line p 2 (Figure 2.5a); as T 2 >T 2s then 2s > 2 . From continuity
P m/A D c and since we are dealing with the same area, c 2 >c 2s , and the kinetic
energy terms are not equal. The difference in practice is usually negligible and often
ignored.
There are several ways of expressing efficiency, the choice of definition depending
largely upon whether the exit kinetic energy is usefully employed or is wasted. An
example where the exhaust kinetic energy is not wasted is from the last stage of
an aircraft gas turbine where it contributes to the jet propulsive thrust. Likewise,
the exit kinetic energy from one stage of a multistage turbine where it is used in
the next stage, provides another example. For these two cases the turbine and stage
adiabatic efficiency , is the total-to-total efficiency and is defined as
h 02s /. (2.21)
tt D W x /W x max D .h 01 h 02 //.h 01