Page 68 - Fluid Catalytic Cracking Handbook
P. 68
4§ Fluid Catalytic Cracking Handbook
Since °API gravity is inversely proportional to specific gravity, the
higher the °API gravity, the lighter the liquid sample. In petroleum
refining, °API gravity is routinely measured for every feed and product
stream. The ASTM D-287 is a hydrometer test typically performed by
a lab technician or unit operator. The method involves inserting a glass
hydrometer into a cylinder containing the sample and reading the °AP1
gravity and the fluid temperature on the hydrometer scale. Standard
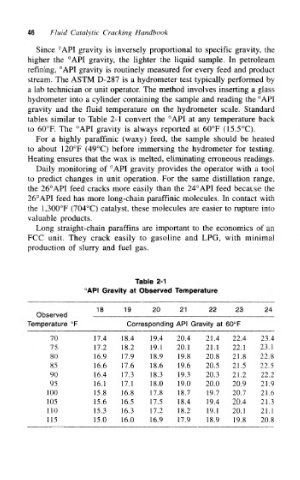
tables similar to Table 2-1 convert the °API at any temperature back
to 60°R The °API gravity is always reported at 60°F (15.5°C).
For a highly paraffinic (waxy) feed, the sample should be heated
to about 120°F (49°C) before immersing the hydrometer for testing.
Heating ensures that the wax is melted, eliminating erroneous readings.
Daily monitoring of °API gravity provides the operator with a tool
to predict changes in unit operation. For the same distillation range,
the 26°API feed cracks more easily than the 24°API feed because the
26°API feed has more long-chain paraffinic molecules. In contact with
the 1,300°F (704°C) catalyst, these molecules are easier to rupture into
valuable products.
Long straight-chain paraffins are important to the economics of an
FCC unit. They crack easily to gasoline and LPG, with minimal
production of slurry and fuel gas.
Table 2-1
API Gravity at Observed Temperature
18 19 20 21 22 23 24
Observed
Temperature °F Corresponding API Gravity at 60°F
70 17.4 18.4 19.4 20.4 21.4 22.4 23.4
75 17.2 18.2 19.1 20.1 21.1 22.1 23.1
80 16.9 17.9 18.9 19.8 20.8 21.8 22.8
85 16.6 17.6 18.6 19.6 20.5 21.5 22.5
90 16.4 17.3 18.3 19.3 20.3 21.2 22.2
95 16.1 17.1 18.0 19.0 20.0 20.9 21.9
100 15.8 16.8 17.8 18.7 19.7 20.7 21.6
105 15.6 16.5 17.5 18.4 19.4 20.4 21.3
110 15.3 16.3 17.2 18.2 19.1 20.1 21.1
115 15.0 16.0 16.9 17.9 18.9 19.8 20.8