Page 128 - Fluid mechanics, heat transfer, and mass transfer
P. 128
106 PUMPS, EJECTORS, BLOWERS, AND COMPRESSORS
. What types of impellers are used in centrifugal pumps
(based on flow direction) for (i) high heads, (ii) inter-
mediate heads, and (iii) low heads?
i. Radial flow impellers are used for high heads.
ii. Mixed flow impellers are used for intermediate
heads.
iii. Axial flow impellers are used for low heads.
. What is the main application of an axial flow (propeller)
pump?
& Very high capacity and low head applications.
& Used in closed loop circulation systems.
. What are the different types of casings used in a
centrifugal pump?
& Circular casing: Involve higher losses due to eddies
and shock when liquid leaves impeller at high ve-
locity. Used for low heads and high capacity.
& Volute casing: It is in the form of a spiral increasing
uniformly in cross-sectional area toward the outlet.
The volute decelerates the liquid, and its velocity is
converted to pressure, efficiently as in a venturi FIGURE 5.7 Suction head and suction lift for a centrifugal pump.
meter. The volute constitutes the casing of the pump.
Used for higher heads and lower capacities.
& Diffuser casing: Turbine pumps—Guide vanes (dif- & Head applies to any liquid that is pumped at the same
fusers) are interposed between impeller discharge rated capacity and speed, as long as the viscosity is
and casing chamber; losses are kept to the minimum low (<10 cP). The head developed by a pump will
and improved efficiency is obtained over a wider remain constant (at a given flow rate and speed), even
range of capacities. This construction is often used though pressure differential and power requirements
in multistage high head pumps. These pumps are vary.
relatively inflexible and often unsatisfactory for . What is TDH?
low flows.
& TDH is the total dynamic head, the energy that the
. Are centrifugal pumps available as multistage units?
pump imparts to the liquid. TDH takes into account
What is their principal advantage over positivedisplace- differences in pressure, liquid elevation and veloc-
ment pumps? ity between the source and the destination, line
& Yes.Multistagingincreases delivery pressures, which frictional losses, and pressure drop through the
is a limitation for single-stage units, while retaining instrumentation and other items in the flow path
their high-capacity capability. Capacities of positive of the liquid.
displacement pumps are generally low although their & It is composed of up to four heads or pressures:
discharge pressures are high. ➢ Static head or the change in elevation of the
& Radial multistage impellers should be operated at liquid across the system. It is the difference in
maximum available rpm, because head per stage the liquid surface level at the suction source or
varies with square of the speed. vessel, subtracted from the liquid surface level
& Invery high head services, such as boiler feed pumps, where the pump delivers the liquid. Some sys-
it may be economical to use a booster pump to handle tems do not have static head or elevation
low NPSH (discussed later) to permit use of a rela- change.
tively small high-speed multistage unit. ➢ Pressure head or the change in pressure across the
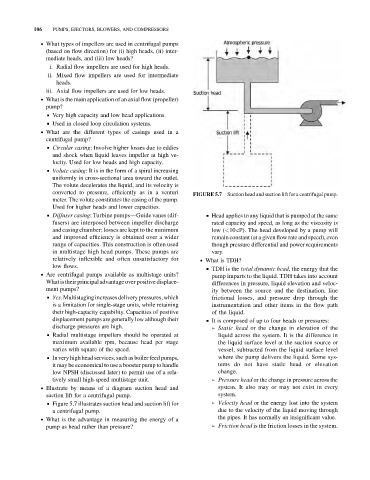
. Illustrate by means of a diagram suction head and system. It also may or may not exist in every
suction lift for a centrifugal pump. system.
& Figure 5.7 illustrates suction head and suction lift for ➢ Velocity head or the energy lost into the system
a centrifugal pump. due to the velocity of the liquid moving through
. What is the advantage in measuring the energy of a the pipes. It has normally an insignificant value.
pump as head rather than pressure? ➢ Friction head is the friction losses in the system.