Page 60 - Fluid mechanics, heat transfer, and mass transfer
P. 60
FRICTION AND PIPING 37
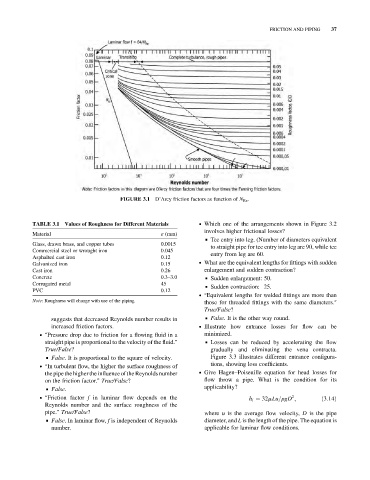
D’Arcy friction factors as function of N Re .
FIGURE 3.1
. Which one of the arrangements shown in Figure 3.2
TABLE 3.1 Values of Roughness for Different Materials
involves higher frictional losses?
Material « (mm)
& Tee entry into leg. (Number of diameters equivalent
Glass, drawn brass, and copper tubes 0.0015
to straight pipe for tee entry into leg are 90, while tee
Commercial steel or wrought iron 0.045
entry from leg are 60.
Asphalted cast iron 0.12
Galvanized iron 0.15 . What are the equivalent lengths for fittings with sudden
Cast iron 0.26 enlargement and sudden contraction?
Concrete 0.3–3.0 & Sudden enlargement: 50.
Corrugated metal 45
& Sudden contraction: 25.
PVC 0.12
. Equivalent lengths for welded fittings are more than
Note: Roughness will change with use of the piping. those for threaded fittings with the same diameters.
True/False?
suggests that decreased Reynolds number results in & False. It is the other way round.
increased friction factors. . Illustrate how entrance losses for flow can be
. Pressure drop due to friction for a flowing fluid in a minimized.
straight pipe is proportional to the velocity of the fluid. & Losses can be reduced by accelerating the flow
True/False? gradually and eliminating the vena contracta.
& False. It is proportional to the square of velocity. Figure 3.3 illustrates different entrance configura-
tions, showing loss coefficients.
. In turbulent flow, the higher the surface roughness of
the pipe the higher the influence of the Reynolds number . Give Hagen–Poiseuille equation for head losses for
on the friction factor. True/False? flow throw a pipe. What is the condition for its
& False. applicability?
. Friction factor f in laminar flow depends on the h f ¼ 32mLu=rgD ; ð3:14Þ
2
Reynolds number and the surface roughness of the
pipe. True/False? where u is the average flow velocity, D is the pipe
& False. In laminar flow, f is independent of Reynolds diameter, and L is the length of the pipe. The equation is
number. applicable for laminar flow conditions.