Page 353 - Subyek Teknik Mesin - Forsthoffers Best Practice Handbook for Rotating Machinery by William E Forsthoffer
P. 353
Be st Practice 6 .2 Gas Turbine Best Practices
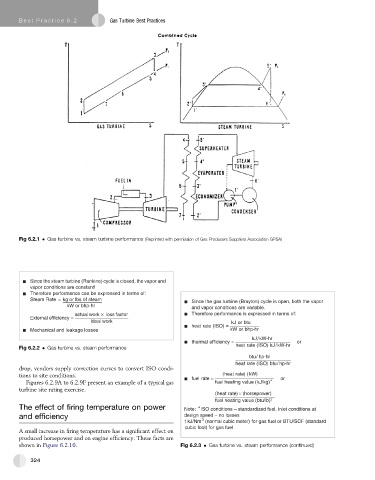
Fig 6.2.1 Gas turbine vs. steam turbine performance (Reprinted with permission of Gas Producers Suppliers Association GPSA)
Since the steam turbine (Rankine) cycle is closed, the vapor and
vapor conditions are constant!
Therefore performance can be expressed in terms of:
Steam Rate = kg or lbs of steam Since the gas turbine (Brayton) cycle is open, both the vapor
kW or bhp-hr and vapor conditions are variable.
actual work loss factor Therefore performance is expressed in terms of:
External efficiency =
ideal work kJ or btu
heat rate (ISO) =
Mechanical and leakage losses kW or bhp-hr
kJ/kW-hr
thermal efficiency = or
Fig 6.2.2 Gas turbine vs. steam performance heat rate (ISO) kJ/kW-hr
btu/ hp-hr
heat rate (ISO) btu/ hp-hr
drop, vendors supply correction curves to convert ISO condi-
tions to site conditions. (heat rate) (kW)
fuel rate = or
Figures 6.2.9A to 6.2.9F present an example of a typical gas fuel heating value (kJ/kg)
turbine site rating exercise.
(heat rate) (horsepower)
fuel heating value (btu/lb)
The effect of firing temperature on power Note: ISO conditions – standardized fuel, inlet conditions at
and efficiency design speed – no losses
3
kJ/Nm (normal cubic meter) for gas fuel or BTU/SCF (standard
cubic foot) for gas fuel
A small increase in firing temperature has a significant effect on
produced horsepower and on engine efficiency. These facts are
shown in Figure 6.2.10. Fig 6.2.3 Gas turbine vs. steam performance (continued)
324