Page 350 - Subyek Teknik Mesin - Forsthoffers Best Practice Handbook for Rotating Machinery by William E Forsthoffer
P. 350
Gas Turbine Best Practices Be st Practice 6.1
coupling environment is significantly reduced in terms of tem-
perature. This results in a much lower axial expansion of the
drive coupling and subsequently increases the reliability of the
gas turbine.
Gas turbine cycles
Gas turbine cycles are presented in Figure 6.1.21. There are
essentially three types of gas turbine cycles: first is the simple
cycle, where the gas is exhausted directly to atmosphere;
secondly, the regenerative cycle, where the exhaust gas is used
in an exchanger (regenerator) to preheat the compressor dis-
charge air prior to the combustor; and finally there is the
combined cycle, where the exhaust gas is used in a heat re-
covery steam generator (HRSG) to either generate steam for
plant use or as an expansion fluid is a steam turbine. Typical
efficiencies are as follows:
- Simple cycle 20% to 43%
- Regenerative cycle 30% to 45%
- Combined cycle 55% to 60%
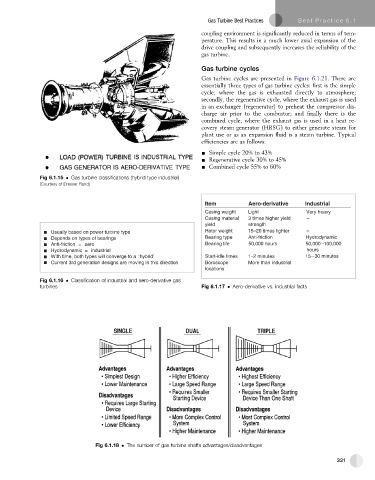
Fig 6.1.15 Gas turbine classifications (hybrid type industrial)
(Courtesy of Dresser Rand)
Item Aero-derivative Industrial
Casing weight Light Very heavy
Casing material 3 times higher yield –
yield strength
Usually based on power turbine type Rotor weight 15–20 times lighter –
Depends on types of bearings Bearing type Anti-friction Hydrodynamic
Anti-friction = aero Bearing life 50,000 hours 50,000–100,000
Hydrodynamic = industrial hours
With time, both types will converge to a ‘hybrid’ Start-idle times 1–2 minutes 15–30 minutes
Current 3rd generation designs are moving in this direction Boroscope More than industrial
locations
Fig 6.1.16 Classification of industrial and aero-derivative gas
turbines Fig 6.1.17 Aero-derivative vs. industrial facts
Fig 6.1.18 The number of gas turbine shafts advantages/disadvantages
321