Page 345 - Subyek Teknik Mesin - Forsthoffers Best Practice Handbook for Rotating Machinery by William E Forsthoffer
P. 345
Be st Practice 6 .1 Gas Turbine Best Practices
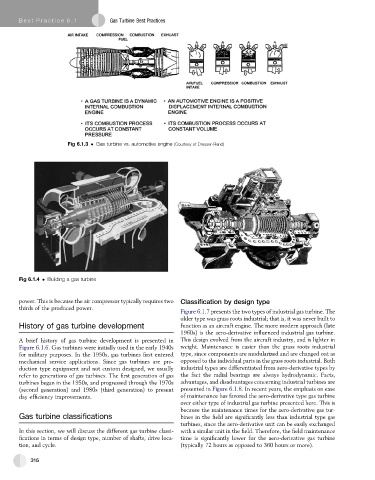
Fig 6.1.3 Gas turbine vs. automotive engine (Courtesy of Dresser-Rand)
Fig 6.1.4 Building a gas turbine
power. This is because the air compressor typically requires two Classification by design type
thirds of the produced power.
Figure 6.1.7 presents the two types of industrial gas turbine. The
older type was grass roots industrial; that is, it was never built to
History of gas turbine development function as an aircraft engine. The more modern approach (late
1960s) is the aero-derivative influenced industrial gas turbine.
A brief history of gas turbine development is presented in This design evolved from the aircraft industry, and is lighter in
Figure 6.1.6. Gas turbines were initially used in the early 1940s weight. Maintenance is easier than the grass roots industrial
for military purposes. In the 1950s, gas turbines first entered type, since components are modularized and are changed out as
mechanical service applications. Since gas turbines are pro- opposed to the individual parts in the grass roots industrial. Both
duction type equipment and not custom designed, we usually industrial types are differentiated from aero-derivative types by
refer to generations of gas turbines. The first generation of gas the fact the radial bearings are always hydrodynamic. Facts,
turbines began in the 1950s, and progressed through the 1970s advantages, and disadvantages concerning industrial turbines are
(second generation) and 1980s (third generation) to present presented in Figure 6.1.8. In recent years, the emphasis on ease
day efficiency improvements. of maintenance has favored the aero-derivative type gas turbine
over either type of industrial gas turbine presented here. This is
because the maintenance times for the aero-derivative gas tur-
Gas turbine classifications bines in the field are significantly less than industrial type gas
turbines, since the aero-derivative unit can be easily exchanged
In this section, we will discuss the different gas turbine classi- with a similar unit in the field. Therefore, the field maintenance
fications in terms of design type, number of shafts, drive loca- time is significantly lower for the aero-derivative gas turbine
tion, and cycle. (typically 72 hours as opposed to 360 hours or more).
316