Page 347 - Subyek Teknik Mesin - Forsthoffers Best Practice Handbook for Rotating Machinery by William E Forsthoffer
P. 347
Be st Practice 6 .1 Gas Turbine Best Practices
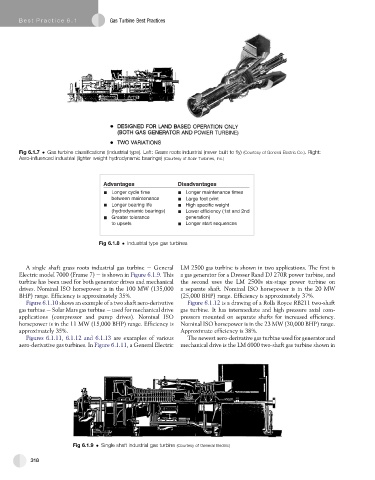
Fig 6.1.7 Gas turbine classifications (industrial type). Left: Grass roots industrial (never built to fly) (Courtesy of General Electric Co.). Right:
Aero-influenced industrial (lighter weight hydrodynamic bearings) (Courtesy of Solar Turbines, Inc.)
Advantages Disadvantages
Longer cycle time Longer maintenance times
between maintenance Large foot print
Longer bearing life High specific weight
(hydrodynamic bearings) Lower efficiency (1st and 2nd
Greater tolerance generation)
to upsets Longer start sequences
Fig 6.1.8 Industrial type gas turbines
A single shaft grass roots industrial gas turbine e General LM 2500 gas turbine is shown in two applications. The first is
Electric model 7000 (Frame 7) e is shown in Figure 6.1.9. This a gas generator for a Dresser Rand DJ 270R power turbine, and
turbine has been used for both generator drives and mechanical the second uses the LM 2500s six-stage power turbine on
drives. Nominal ISO horsepower is in the 100 MW (135,000 a separate shaft. Nominal ISO horsepower is in the 20 MW
BHP) range. Efficiency is approximately 35%. (25,000 BHP) range. Efficiency is approximately 37%.
Figure 6.1.10 shows an example of a two shaft aero-derivative Figure 6.1.12 is a drawing of a Rolls Royce RB211 two-shaft
gas turbine e Solar Mars gas turbine e used for mechanical drive gas turbine. It has intermediate and high pressure axial com-
applications (compressor and pump drives). Nominal ISO pressors mounted on separate shafts for increased efficiency.
horsepower is in the 11 MW (15,000 BHP) range. Efficiency is Nominal ISO horsepower is in the 23 MW (30,000 BHP) range.
approximately 35%. Approximate efficiency is 38%.
Figures 6.1.11, 6.1.12 and 6.1.13 are examples of various The newest aero-derivative gas turbine used for generator and
aero-derivative gas turbines. In Figure 6.1.11, a General Electric mechanical drive is the LM 6000 two-shaft gas turbine shown in
Fig 6.1.9 Single shaft industrial gas turbine (Courtesy of General Electric)
318