Page 137 - From Smart Grid to Internet of Energy
P. 137
Power line communication technologies in smart grids Chapter 4 121
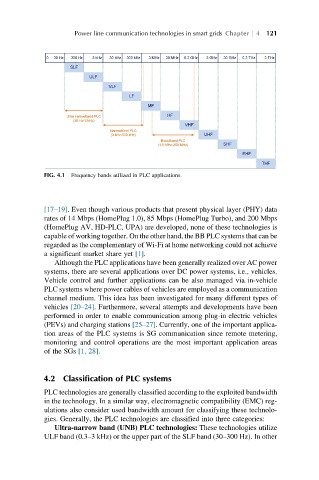
FIG. 4.1 Frequency bands utilized in PLC applications.
[17–19]. Even though various products that present physical layer (PHY) data
rates of 14 Mbps (HomePlug 1.0), 85 Mbps (HomePlug Turbo), and 200 Mbps
(HomePlug AV, HD-PLC, UPA) are developed, none of these technologies is
capable of working together. On the other hand, the BB PLC systems that can be
regarded as the complementary of Wi-Fi at home networking could not achieve
a significant market share yet [1].
Although the PLC applications have been generally realized over AC power
systems, there are several applications over DC power systems, i.e., vehicles.
Vehicle control and further applications can be also managed via in-vehicle
PLC systems where power cables of vehicles are employed as a communication
channel medium. This idea has been investigated for many different types of
vehicles [20–24]. Furthermore, several attempts and developments have been
performed in order to enable communication among plug-in electric vehicles
(PEVs) and charging stations [25–27]. Currently, one of the important applica-
tion areas of the PLC systems is SG communication since remote metering,
monitoring and control operations are the most important application areas
of the SGs [1, 28].
4.2 Classification of PLC systems
PLC technologies are generally classified according to the exploited bandwidth
in the technology. In a similar way, electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) reg-
ulations also consider used bandwidth amount for classifying these technolo-
gies. Generally, the PLC technologies are classified into three categories:
Ultra-narrow band (UNB) PLC technologies: These technologies utilize
ULF band (0.3–3 kHz) or the upper part of the SLF band (30–300 Hz). In other