Page 348 - From Smart Grid to Internet of Energy
P. 348
312 From smart grid to internet of energy
8.2 Overview of big data
It is noted that Big data has been proposed by McKinsey in a report with
definition of its size, storage, and management methods. It has been accepted
as a new method facilitating technological innovations and leveraging the
economic growth. On the other hand, big data does not refer to just data masses
of several TBs. The fundamental approach behind the data processing is
generation and distribution of smart intelligence among huge numbers of com-
puters, server, and service providers. The big data analysis cycle is comprised
by data acquisition, data storage and management, data modeling, data mining
and data processing steps [4, 5]. One of the most widely used open-source data
analysis tool is known as Hadoop which is benefited by Siemens, ABB, General
Electric, IBM, Facebook, Microsoft, Google, HP, Yahoo, Netflix, Amazon and
many more [4]. The popular application of Hadoop is MapReduce technology
and it facilitates the data analysis among large amounts of databases. The big
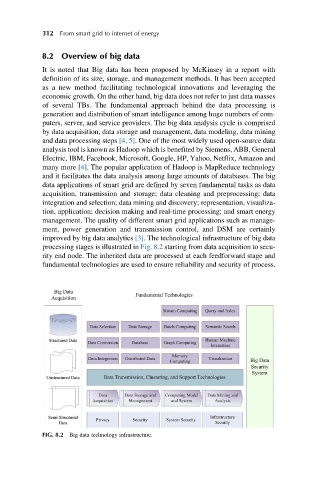
data applications of smart grid are defined by seven fundamental tasks as data
acquisition, transmission and storage; data cleaning and preprocessing; data
integration and selection; data mining and discovery; representation, visualiza-
tion, application; decision making and real-time processing; and smart energy
management. The quality of different smart grid applications such as manage-
ment, power generation and transmission control, and DSM are certainly
improved by big data analytics [3]. The technological infrastructure of big data
processing stages is illustrated in Fig. 8.2 starting from data acquisition to secu-
rity end node. The inherited data are processed at each feedforward stage and
fundamental technologies are used to ensure reliability and security of process.
FIG. 8.2 Big data technology infrastructure.