Page 36 - From Smart Grid to Internet of Energy
P. 36
Introduction to smart grid and internet of energy systems Chapter 1 25
while other types that are not including synchronous generator are PV plants,
biomass plants, fuel cells, and batteries. The expressed generator structures
require some featured control systems to ensure the stability and quality of volt-
age, frequency, active and reactive power of microgrid system. These are
directly related to microgrid operation, control, and protection issues that will
be introduced in detail in the following chapters.
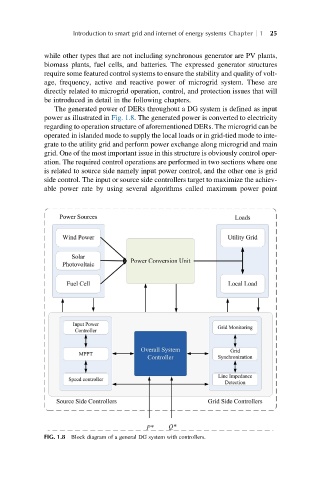
The generated power of DERs throughout a DG system is defined as input
power as illustrated in Fig. 1.8. The generated power is converted to electricity
regarding to operation structure of aforementioned DERs. The microgrid can be
operated in islanded mode to supply the local loads or in grid-tied mode to inte-
grate to the utility grid and perform power exchange along microgrid and main
grid. One of the most important issue in this structure is obviously control oper-
ation. The required control operations are performed in two sections where one
is related to source side namely input power control, and the other one is grid
side control. The input or source side controllers target to maximize the achiev-
able power rate by using several algorithms called maximum power point
FIG. 1.8 Block diagram of a general DG system with controllers.