Page 147 - Fundamentals of Air Pollution
P. 147
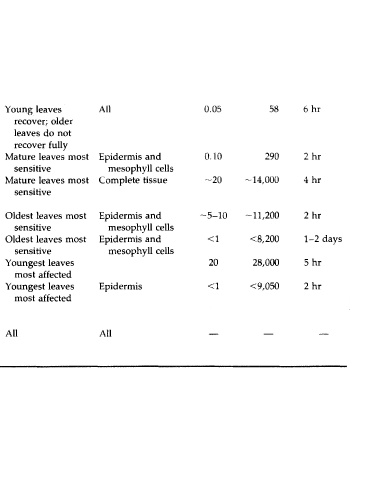
Ethylene Sepal withering, leaf abnormalities; flower Young leaves All 0.05 58 6hr
dropping, and failure of leaf to open properly; recover; older
abscission; water stress may produce similar leaves do not
markings recover fully
Chlorine Bleaching between veins, tip and margin burn, leaf Mature leaves most Epidermis and 0.10 290 2 hr
abscission; marking often similar to that of ozone sensitive mesophyll cells
Ammonia "Cooked" green appearance becoming brown or Mature leaves most Complete tissue ~20 -14,000 4 hr
green on drying; overall blackening on some sensitive
species
Hydrogen Acid-type necrotic lesion; tip burn on fir needles; Oldest leaves most Epidermis and -5-10 -11,200 2 hr
chloride leaf margin necrosis on broad leaves sensitive mesophyll cells
Mercury Chlorosis and abscission; brown spotting; Oldest leaves most Epidermis and <1 <8,200 1-2 days
yellowing of veins sensitive mesophyll cells
Hydrogen Basal and marginal scorching Youngest leaves 20 28,000 5 hr
sulfide most affected
2,4-Dichloro- Scalloped margins, swollen stems, yellow-green Youngest leaves Epidermis <1 <9,050 2 hr
phenoxy- mottling or stippling, suture red spot (2,4,5-T); most affected
acetic acid epinasty
(2-4D)
Sulfuric acid Necrotic spots on upper surface similar to those All AH — — —
caused by caustic or acidic compounds; high
humidity needed