Page 47 - Fundamentals of Enhanced Oil and Gas Recovery
P. 47
An Introduction to Enhanced Oil Recovery 35
Primary
Natural flow Secondary Artificial lift
Waterflood Tertiary Pressure maintenance
Chemical Thermal Miscible Microbial, electrical, chemical
leaching, mechanical
Surfactant Polymer Caustic
CO 2 Miscible solvent Inert gas
In-situ
Steam or
Steam stimulation combustion
hot water
Or cyclic steam injection
Foam displacement
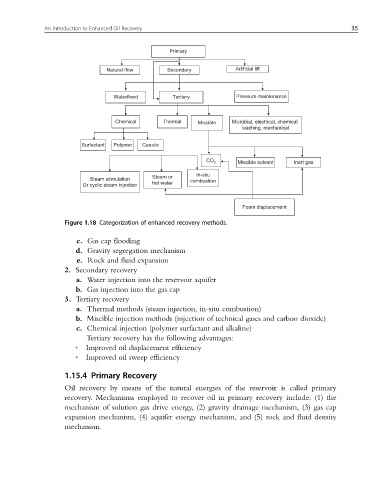
Figure 1.18 Categorization of enhanced recovery methods.
c. Gas cap flooding
d. Gravity segregation mechanism
e. Rock and fluid expansion
2. Secondary recovery
a. Water injection into the reservoir aquifer
b. Gas injection into the gas cap
3. Tertiary recovery
a. Thermal methods (steam injection, in-situ combustion)
b. Miscible injection methods (injection of technical gases and carbon dioxide)
c. Chemical injection (polymer surfactant and alkaline)
Tertiary recovery has the following advantages:
• Improved oil displacement efficiency
• Improved oil sweep efficiency
1.15.4 Primary Recovery
Oil recovery by means of the natural energies of the reservoir is called primary
recovery. Mechanisms employed to recover oil in primary recovery include: (1) the
mechanism of solution gas drive energy, (2) gravity drainage mechanism, (3) gas cap
expansion mechanism, (4) aquifer energy mechanism, and (5) rock and fluid density
mechanism.