Page 185 - Fundamentals of Geomorphology
P. 185
168 PROCESS AND FORM
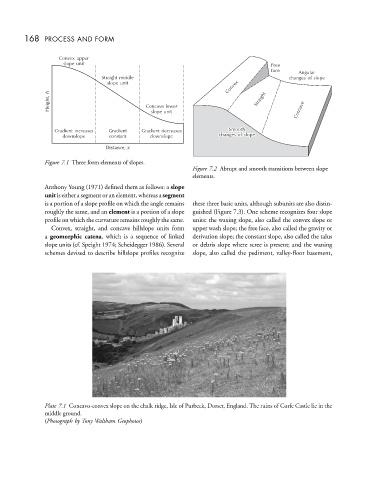
Convex upper
slope unit Free
face Angular
Straight middle changes of slope
Convex
Convex
slope unit
Straight
h
Height, Concave lower Straight Concave
Concave
slope unit
Smooth
Gradient increases Gradient Gradient decreases Smooth
of
changes
slope
downslope constant downslope changes of slope
Distance, x
Figure 7.1 Three form elements of slopes.
Figure 7.2 Abrupt and smooth transitions between slope
elements.
Anthony Young (1971) defined them as follows: a slope
unit is either a segment or an element, whereas a segment
is a portion of a slope profile on which the angle remains these three basic units, although subunits are also distin-
roughly the same, and an element is a portion of a slope guished (Figure 7.3). One scheme recognizes four slope
profile on which the curvature remains roughly the same. units: the waxing slope, also called the convex slope or
Convex, straight, and concave hillslope units form upper wash slope; the free face, also called the gravity or
a geomorphic catena, which is a sequence of linked derivation slope; the constant slope, also called the talus
slope units (cf. Speight 1974; Scheidegger 1986). Several or debris slope where scree is present; and the waning
schemes devised to describe hillslope profiles recognize slope, also called the pediment, valley-floor basement,
Plate 7.1 Concavo-convex slope on the chalk ridge, Isle of Purbeck, Dorset, England. The ruins of Corfe Castle lie in the
middle ground.
(Photograph by Tony Waltham Geophotos)