Page 205 - Fundamentals of Geomorphology
P. 205
188 PROCESS AND FORM
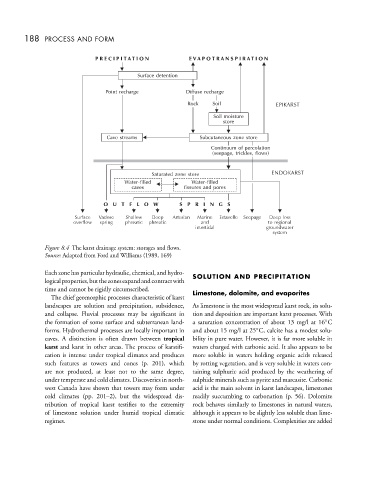
Figure 8.4 The karst drainage system: storages and flows.
Source: Adapted from Ford and Williams (1989, 169)
Each zone has particular hydraulic, chemical, and hydro- SOLUTION AND PRECIPITATION
logicalproperties,butthezonesexpandandcontractwith
time and cannot be rigidly circumscribed. Limestone, dolomite, and evaporites
The chief geomorphic processes characteristic of karst
landscapes are solution and precipitation, subsidence, As limestone is the most widespread karst rock, its solu-
and collapse. Fluvial processes may be significant in tion and deposition are important karst processes. With
the formation of some surface and subterranean land- a saturation concentration of about 13 mg/l at 16 C
◦
forms. Hydrothermal processes are locally important in and about 15 mg/l at 25 C, calcite has a modest solu-
◦
caves. A distinction is often drawn between tropical bility in pure water. However, it is far more soluble in
karst and karst in other areas. The process of karstifi- waters charged with carbonic acid. It also appears to be
cation is intense under tropical climates and produces more soluble in waters holding organic acids released
such features as towers and cones (p. 201), which by rotting vegetation, and is very soluble in waters con-
are not produced, at least not to the same degree, taining sulphuric acid produced by the weathering of
under temperate and cold climates. Discoveries in north- sulphide minerals such as pyrite and marcasite. Carbonic
west Canada have shown that towers may form under acid is the main solvent in karst landscapes, limestones
cold climates (pp. 201–2), but the widespread dis- readily succumbing to carbonation (p. 56). Dolomite
tribution of tropical karst testifies to the extremity rock behaves similarly to limestones in natural waters,
of limestone solution under humid tropical climatic although it appears to be slightly less soluble than lime-
regimes. stone under normal conditions. Complexities are added