Page 207 - Fundamentals of Geomorphology
P. 207
190 PROCESS AND FORM
SURFACE KARST FORMS unimpeded to the sea, and impounded karst, which is
surroundedbyimperviousrocksandhastodrainthrough
Early studies of karst landscapes centred on Vienna, with different hydrogeological systems to reach the sea.
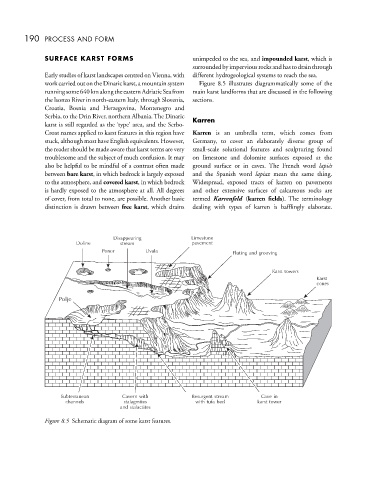
work carried out on the Dinaric karst, a mountain system Figure 8.5 illustrates diagrammatically some of the
runningsome640kmalongtheeasternAdriaticSeafrom main karst landforms that are discussed in the following
the Isonzo River in north-eastern Italy, through Slovenia, sections.
Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro and
Serbia, to the Drin River, northern Albania. The Dinaric Karren
karst is still regarded as the ‘type’ area, and the Serbo-
Croat names applied to karst features in this region have Karren is an umbrella term, which comes from
stuck, although most have English equivalents. However, Germany, to cover an elaborately diverse group of
the reader should be made aware that karst terms are very small-scale solutional features and sculpturing found
troublesome and the subject of much confusion. It may on limestone and dolomite surfaces exposed at the
also be helpful to be mindful of a contrast often made ground surface or in caves. The French word lapiés
between bare karst, in which bedrock is largely exposed and the Spanish word lapiaz mean the same thing.
to the atmosphere, and covered karst, in which bedrock Widespread, exposed tracts of karren on pavements
is hardly exposed to the atmosphere at all. All degrees and other extensive surfaces of calcareous rocks are
of cover, from total to none, are possible. Another basic termed Karrenfeld (karren fields). The terminology
distinction is drawn between free karst, which drains dealing with types of karren is bafflingly elaborate.
Figure 8.5 Schematic diagram of some karst features.