Page 297 - Fundamentals of Geomorphology
P. 297
280 PROCESS AND FORM
North Continuous zone Discontinuous zone South
Permafrost table Active layer
0.5m
3m
10 m
50 m
50 m
ermafrost
P Permafrost
(may
(may be hundreds
hundreds
be
metres
thick)
of metres thick)
of
alik
T Talik
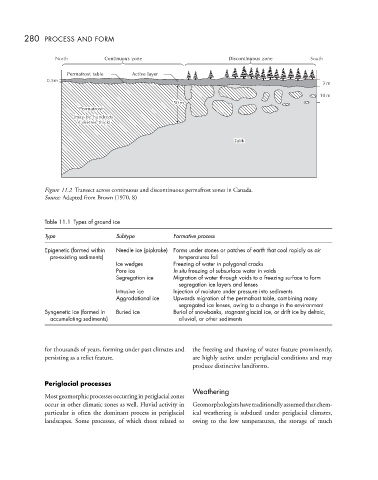
Figure 11.2 Transect across continuous and discontinuous permafrost zones in Canada.
Source: Adapted from Brown (1970, 8)
Table 11.1 Types of ground ice
Type Subtype Formative process
Epigenetic (formed within Needle ice (pipkrake) Forms under stones or patches of earth that cool rapidly as air
pre-existing sediments) temperatures fall
Ice wedges Freezing of water in polygonal cracks
Pore ice In situ freezing of subsurface water in voids
Segregation ice Migration of water through voids to a freezing surface to form
segregation ice layers and lenses
Intrusive ice Injection of moisture under pressure into sediments
Aggradational ice Upwards migration of the permafrost table, combining many
segregated ice lenses, owing to a change in the environment
Syngenetic ice (formed in Buried ice Burial of snowbanks, stagnant glacial ice, or drift ice by deltaic,
accumulating sediments) alluvial, or other sediments
for thousands of years, forming under past climates and the freezing and thawing of water feature prominently,
persisting as a relict feature. are highly active under periglacial conditions and may
produce distinctive landforms.
Periglacial processes
Weathering
Most geomorphic processes occurring in periglacial zones
occur in other climatic zones as well. Fluvial activity in Geomorphologistshavetraditionallyassumedthatchem-
particular is often the dominant process in periglacial ical weathering is subdued under periglacial climates,
landscapes. Some processes, of which those related to owing to the low temperatures, the storage of much