Page 31 - Fundamentals of Geomorphology
P. 31
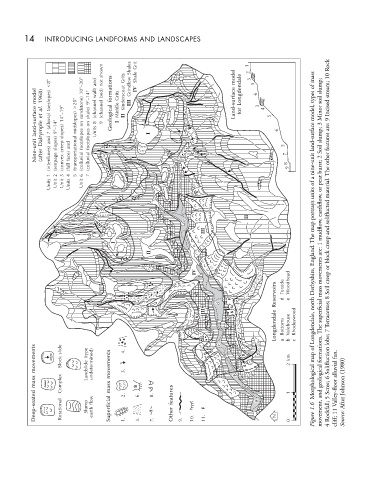
14 INTRODUCING LANDFORMS AND LANDSCAPES
shown Shales Grit 1 2 Rock 10
<8° 10°–20° and not formations Grits Grindlow Shale IV model Longdendale 3 5 mass of slump; stream;
model 1968) al. toeslopes) >20° sandstone) 9°–14° wall) (channel bed) (channel Grits Kinderscout III Land-surface 6 3 4 types soil Incised
land-surface et Dalrymple (alluvial 7 9°–14° 14°–19° slopes) midslopes) on shale) on 8 Units 9 Geological Middle I II I T T T for 5 6 model, Minor 3 slump; 9 are:
Nine-unit (after and (interfluves) slopes) (seepage creep and face) (transportational footslopes (colluvial footslopes (colluvial T T T 5 7 land-surface Soil 2 features other
(convex
(fall
T T 8 9 nine-unit burst;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
a peat
Units Unit Unit Units Unit of material. The
units
S or
portrays earthflow, soliflucted
II
e e
map
III mudflow, and
England. The
I 1 creep
II are: block
IV movements or
Reservoirs mass Soil
F Torside Woodhead Derbyshire, creep
F d e 8
d d north
S
III III S superficial
Longdendale Bottoms a b Valehouse Rhodeswood c Longdendale, lobe;
S 7 Terracettes;
movements slide Block (type Landslide undetermined) movements 4. c c S S S km 2 of map formations. The Solifluction fan. alluvial (1980)
mass Complex mass 3. S b b S 1 Morphological geological and 6 Scree; Valley-floor Johnson
Deep-seated Rotational Slump flow earth Superficial 2. 1. 6. 5. T 8. 7. features Other 9. 10. F 11. a a N 0 1.6 Figure movement, 5 Rockfall; 4 11 cliff; After Source: