Page 348 - Fundamentals of Geomorphology
P. 348
COASTAL LANDSCAPES 331
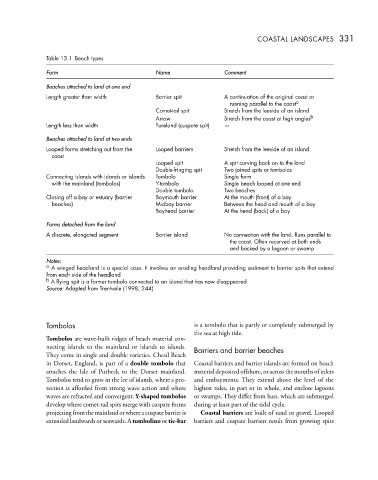
Table 13.1 Beach types
Form Name Comment
Beaches attached to land at one end
Length greater than width Barrier spit A continuation of the original coast or
running parallel to the coast a
Comet-tail spit Stretch from the leeside of an island
Arrow Stretch from the coast at high angles b
Length less than width Foreland (cuspate spit) —
Beaches attached to land at two ends
Looped forms stretching out from the Looped barriers Stretch from the leeside of an island
coast
Looped spit A spit curving back on to the land
Double-fringing spit Two joined spits or tombolos
Connecting islands with islands or islands Tombolo Single form
with the mainland (tombolos) Y-tombolo Single beach looped at one end
Double tombolo Two beaches
Closing off a bay or estuary (barrier Baymouth barrier At the mouth (front) of a bay
beaches) Midbay barrier Between the head and mouth of a bay
Bayhead barrier At the head (back) of a bay
Forms detached from the land
A discrete, elongated segment Barrier island No connection with the land. Runs parallel to
the coast. Often recurved at both ends
and backed by a lagoon or swamp
Notes:
a A winged headland is a special case. It involves an eroding headland providing sediment to barrier spits that extend
from each side of the headland
b A flying spit is a former tombolo connected to an island that has now disappeared
Source: Adapted from Trenhaile (1998, 244)
Tombolos is a tombolo that is partly or completely submerged by
the sea at high tide.
Tombolos are wave-built ridges of beach material con-
necting islands to the mainland or islands to islands. Barriers and barrier beaches
They come in single and double varieties. Chesil Beach
in Dorset, England, is part of a double tombolo that Coastal barriers and barrier islands are formed on beach
attaches the Isle of Purbeck to the Dorset mainland. material deposited offshore, or across the mouths of inlets
Tombolos tend to grow in the lee of islands, where a pro- and embayments. They extend above the level of the
tection is afforded from strong wave action and where highest tides, in part or in whole, and enclose lagoons
waves are refracted and convergent. Y-shaped tombolos or swamps. They differ from bars, which are submerged
develop where comet-tail spits merge with cuspate forms during at least part of the tidal cycle.
projectingfromthemainlandorwhereacuspatebarrieris Coastal barriers are built of sand or gravel. Looped
extended landwards or seawards. A tombolino or tie-bar barriers and cuspate barriers result from growing spits