Page 81 - Fundamentals of Geomorphology
P. 81
64 INTRODUCING LANDFORMS AND LANDSCAPES
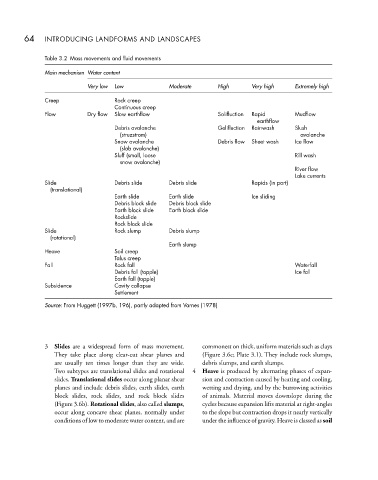
Table 3.2 Mass movements and fluid movements
Main mechanism Water content
Very low Low Moderate High Very high Extremely high
Creep Rock creep
Continuous creep
Flow Dry flow Slow earthflow Solifluction Rapid Mudflow
earthflow
Debris avalanche Gelifluction Rainwash Slush
(struzstrom) avalanche
Snow avalanche Debris flow Sheet wash Ice flow
(slab avalanche)
Sluff (small, loose Rill wash
snow avalanche)
River flow
Lake currents
Slide Debris slide Debris slide Rapids (in part)
(translational)
Earth slide Earth slide Ice sliding
Debris block slide Debris block slide
Earth block slide Earth block slide
Rockslide
Rock block slide
Slide Rock slump Debris slump
(rotational)
Earth slump
Heave Soil creep
Talus creep
Fall Rock fall Waterfall
Debris fall (topple) Ice fall
Earth fall (topple)
Subsidence Cavity collapse
Settlement
Source: From Huggett (1997b, 196), partly adapted from Varnes (1978)
3 Slides are a widespread form of mass movement. commonest on thick, uniform materials such as clays
They take place along clear-cut shear planes and (Figure 3.6c; Plate 3.1). They include rock slumps,
are usually ten times longer than they are wide. debris slumps, and earth slumps.
Two subtypes are translational slides and rotational 4 Heave is produced by alternating phases of expan-
slides. Translational slides occur along planar shear sion and contraction caused by heating and cooling,
planes and include debris slides, earth slides, earth wetting and drying, and by the burrowing activities
block slides, rock slides, and rock block slides of animals. Material moves downslope during the
(Figure 3.6b). Rotational slides, also called slumps, cycles because expansion lifts material at right-angles
occur along concave shear planes, normally under to the slope but contraction drops it nearly vertically
conditions of low to moderate water content, and are under the influence of gravity. Heave is classed as soil