Page 79 - Fundamentals of Geomorphology
P. 79
62 INTRODUCING LANDFORMS AND LANDSCAPES
body is greater than the shear strength, the material will rigid solid and fractures. If gentle pressure is applied to it
fail and move downslope. A scheme for defining the for some time, it behaves as an elastic solid and deforms
intact rock strength (the strength of rock excluding the reversibly before fracturing. Earth materials behave elas-
effects of joints and fractures) has been devised. Intact tically when small stresses are applied to them. Perfect
strength iseasily assessed using a Schmidt hammer,which plastic solids resist deformation until the shear stress
measures the rebound of a known impact from a rock reaches a threshold value called the yield limit. Once
surface. Rock mass strength may be assessed using intact beyond the yield stress, deformation of plastic bodies is
rock strength and other factors (weathering, joint spac- unlimited and they do not revert to their original shape
ing, joint orientations, joint width, joint continuity and once the stress is withdrawn. Liquids include water and
infill, and groundwater outflow). Combining these fac- liquefied soils or sediments, that is, soil and sediments
tors gives a rock mass strength rating ranging from very that behave as fluids.
strong, through strong, moderate, and weak, to very weak An easy way of appreciating the rheology (response
(see Selby 1980). to stress) of different materials is to imagine a rubber
ball, a clay ball, a glob of honey, and a cubic crystal of
Soil behaviour rock salt (cf. Selby 1982, 74). When dropped from the
same height on to a hard floor, the elastic ball deforms
Materials are classed as rigid solids, elastic solids, plastics, on impact but quickly recovers its shape; the plastic clay
or fluids. Each of these classes reacts differently to stress: sticks to the floor as a blob; the viscous honey spreads
they each have a characteristic relationship between the slowly over the floor; and the brittle rock salt crystal
rate of deformation (strain rate) and the applied stress shatters and fragments are strewn over the floor.
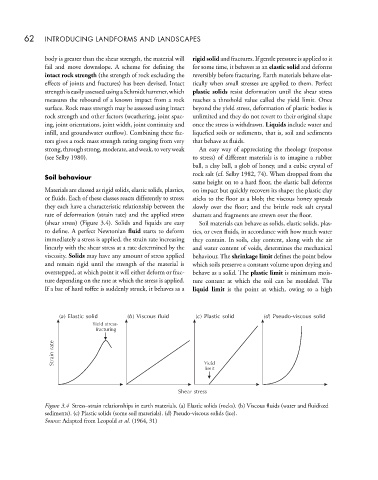
(shear stress) (Figure 3.4). Solids and liquids are easy Soil materials can behave as solids, elastic solids, plas-
to define. A perfect Newtonian fluid starts to deform tics, or even fluids, in accordance with how much water
immediately a stress is applied, the strain rate increasing they contain. In soils, clay content, along with the air
linearly with the shear stress at a rate determined by the and water content of voids, determines the mechanical
viscosity. Solids may have any amount of stress applied behaviour. The shrinkage limit defines the point below
and remain rigid until the strength of the material is which soils preserve a constant volume upon drying and
overstepped, at which point it will either deform or frac- behave as a solid. The plastic limit is minimum mois-
ture depending on the rate at which the stress is applied. ture content at which the soil can be moulded. The
If a bar of hard toffee is suddenly struck, it behaves as a liquid limit is the point at which, owing to a high
Figure 3.4 Stress–strain relationships in earth materials. (a) Elastic solids (rocks). (b) Viscous fluids (water and fluidized
sediments). (c) Plastic solids (some soil materials). (d) Pseudo-viscous solids (ice).
Source: Adapted from Leopold et al. (1964, 31)