Page 271 - Fundamentals of Light Microscopy and Electronic Imaging
P. 271
254 VIDEO MICROSCOPY
100
Percent modulation Diffraction limited MTF
2 4 8
1
f f f
c 1 c 2 c 8
Spatial frequency
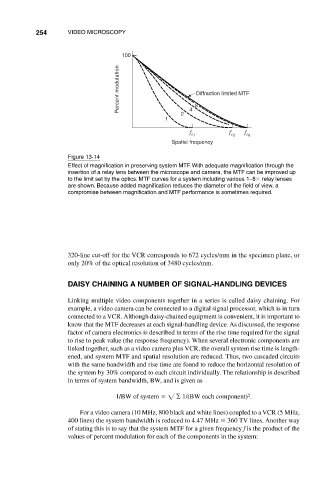
Figure 13-14
Effect of magnification in preserving system MTF. With adequate magnification through the
insertion of a relay lens between the microscope and camera, the MTF can be improved up
to the limit set by the optics. MTF curves for a system including various 1–8 relay lenses
are shown. Because added magnification reduces the diameter of the field of view, a
compromise between magnification and MTF performance is sometimes required.
320-line cut-off for the VCR corresponds to 672 cycles/mm in the specimen plane, or
only 20% of the optical resolution of 3480 cycles/mm.
DAISY CHAINING A NUMBER OF SIGNAL-HANDLING DEVICES
Linking multiple video components together in a series is called daisy chaining. For
example, a video camera can be connected to a digital signal processor, which is in turn
connected to a VCR. Although daisy-chained equipment is convenient, it is important to
know that the MTF decreases at each signal-handling device. As discussed, the response
factor of camera electronics is described in terms of the rise time required for the signal
to rise to peak value (the response frequency). When several electronic components are
linked together, such as a video camera plus VCR, the overall system rise time is length-
ened, and system MTF and spatial resolution are reduced. Thus, two cascaded circuits
with the same bandwidth and rise time are found to reduce the horizontal resolution of
the system by 30% compared to each circuit individually. The relationship is described
in terms of system bandwidth, BW, and is given as
2
1/BW of system 1/(BW each component) .
For a video camera (10 MHz, 800 black and white lines) coupled to a VCR (5 MHz,
400 lines) the system bandwidth is reduced to 4.47 MHz 360 TV lines. Another way
of stating this is to say that the system MTF for a given frequency f is the product of the
values of percent modulation for each of the components in the system: