Page 291 - Fundamentals of Light Microscopy and Electronic Imaging
P. 291
274 DIGITAL CCD MICROSCOPY
80 SITe ST001
Sony ICX 285 back-illuminated
Quantum efficiency (%) 40 Kodak 1401e
60
20 Sony ICX 075
Kodak 1401
Sony ICX 061
0
300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000
Wavelength (nm)
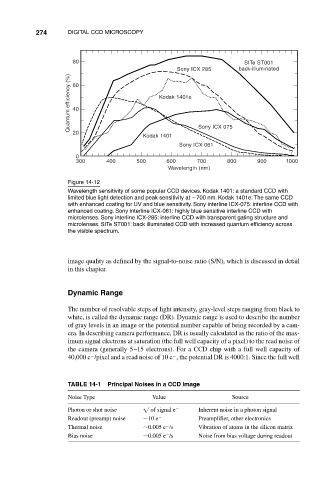
Figure 14-12
Wavelength sensitivity of some popular CCD devices. Kodak 1401: a standard CCD with
limited blue light detection and peak sensitivity at 700 nm. Kodak 1401e: The same CCD
with enhanced coating for UV and blue sensitivity. Sony interline ICX-075: interline CCD with
enhanced coating. Sony interline ICX-061: highly blue sensitive interline CCD with
microlenses. Sony interline ICX-285: interline CCD with transparent gating structure and
microlenses. SITe ST001: back illuminated CCD with increased quantum efficiency across
the visible spectrum.
image quality as defined by the signal-to-noise ratio (S/N), which is discussed in detail
in this chapter.
Dynamic Range
The number of resolvable steps of light intensity, gray-level steps ranging from black to
white, is called the dynamic range (DR). Dynamic range is used to describe the number
of gray levels in an image or the potential number capable of being recorded by a cam-
era. In describing camera performance, DR is usually calculated as the ratio of the max-
imum signal electrons at saturation (the full well capacity of a pixel) to the read noise of
the camera (generally 5–15 electrons). For a CCD chip with a full well capacity of
40,000 e /pixel and a read noise of 10 e , the potential DR is 4000:1. Since the full well
TABLE 14-1 Principal Noises in a CCD Image
Noise Type Value Source
Photon or shot noise of signal e Inherent noise in a photon signal
Readout (preamp) noise 10 e Preamplifier, other electronics
Thermal noise 0.005 e /s Vibration of atoms in the silicon matrix
Bias noise 0.005 e /s Noise from bias voltage during readout