Page 64 - Fundamentals of Light Microscopy and Electronic Imaging
P. 64
OBJECT-IMAGE MATH 47
Lens
F F
Object
(a)
Rear focal
point
F F
(b)
Axis
F F
(c)
Image
F
F
Object
(d)
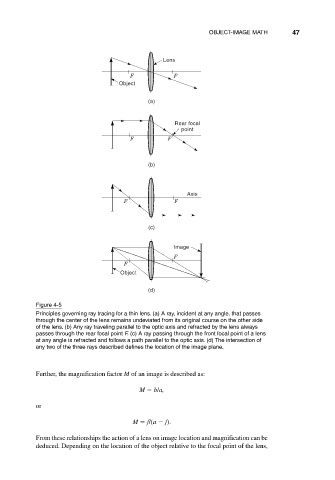
Figure 4-5
Principles governing ray tracing for a thin lens. (a) A ray, incident at any angle, that passes
through the center of the lens remains undeviated from its original course on the other side
of the lens. (b) Any ray traveling parallel to the optic axis and refracted by the lens always
passes through the rear focal point F. (c) A ray passing through the front focal point of a lens
at any angle is refracted and follows a path parallel to the optic axis. (d) The intersection of
any two of the three rays described defines the location of the image plane.
Further, the magnification factor M of an image is described as:
M b/a,
or
M f/(a f).
From these relationships the action of a lens on image location and magnification can be
deduced. Depending on the location of the object relative to the focal point of the lens,