Page 338 - Fundamentals of Magnetic Thermonuclear Reactor Design
P. 338
Blanket Chapter | 10 315
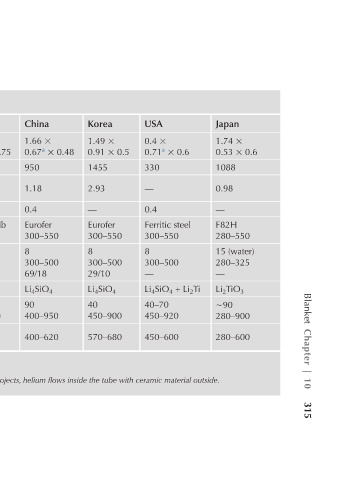
Japan 1.74 × 0.53 × 0.6 1088 0.98 — F82H 280–550 15 (water) 280–325 — Li 2 TiO 3 ∼90 280–900 280–600
USA 0.4 × 0.71 a × 0.6 330 — 0.4 Ferritic steel 300–550 8 300–500 — Li 4 SiO 4 + Li 2 Ti 40–70 450–920 450–600
Korea 1.49 × 0.91 × 0.5 1455 2.93 — Eurofer 300–550 8 300–500 29/10 Li 4 SiO 4 40 450–900 570–680
China 1.66 × 0.67 a × 0.48 950 1.18 0.4 Eurofer 300–550 8 300–500 69/18 Li 4 SiO 4 90 400–950 400–620
Russia 0.84 × 0.51 a × 0.75 446 0.92 0.5 9CrMoVNb 300–550 8 300–500 19/7 Li 4 SiO 4 30–90 400–1000 400–550 c In the Russian project, helium washes the tube housing the ceramic material; in other projects, helium flows inside the tube with ceramic material outside.
TABLE 10.5 Characteristics of Helium-Cooled Ceramic TBMs
Japan 1.29 × 0.76 × 0.6 1162 1.08 — F82H 280–550 8 300–500 35/14 Li 2 TiO 3 ∼90 280–900 280–600
1.27 × 0.74 × 0.7 Eurofer 300–550 300–500 Li 4 SiO 4 40–90 450–920 450–600
EU 950 1.16 0.4 8 85/35
(poloidal × toroidal × radial) Power released in TBM (kW) Tritium breeding rate, peak value Coolant (He) pressure (MPa) Ceramics temperature range (°C) Temperature range of neutron a Submodules with dimensions smaller than the port. b First value refers to the FW, second value refers to the BZ.
Parameters Dimensions (m) (µg/s) BZ radial dimension (m) Structural material, temperature range (°C) Temperature range (°C) Flow rate b (m/s) Ceramic material c 6 Li enrichment (%) multiplier (Be) (°C)