Page 28 - Fundamentals of Ocean Renewable Energy Generating Electricity From The Sea
P. 28
Introduction Chapter | 1 19
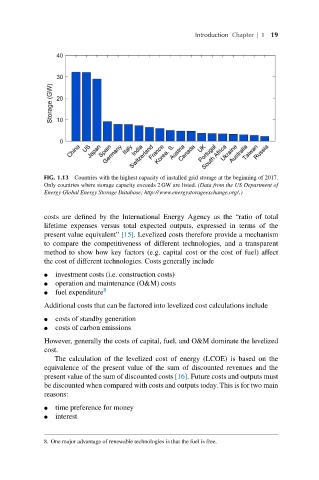
FIG. 1.13 Countries with the highest capacity of installed grid storage at the beginning of 2017.
Only countries where storage capacity exceeds 2 GW are listed. (Data from the US Department of
Energy Global Energy Storage Database; http://www.energystorageexchange.org/.)
costs are defined by the International Energy Agency as the “ratio of total
lifetime expenses versus total expected outputs, expressed in terms of the
present value equivalent” [15]. Levelized costs therefore provide a mechanism
to compare the competitiveness of different technologies, and a transparent
method to show how key factors (e.g. capital cost or the cost of fuel) affect
the cost of different technologies. Costs generally include
● investment costs (i.e. construction costs)
● operation and maintenance (O&M) costs
● fuel expenditure 8
Additional costs that can be factored into levelized cost calculations include
● costs of standby generation
● costs of carbon emissions
However, generally the costs of capital, fuel, and O&M dominate the levelized
cost.
The calculation of the levelized cost of energy (LCOE) is based on the
equivalence of the present value of the sum of discounted revenues and the
present value of the sum of discounted costs [16]. Future costs and outputs must
be discounted when compared with costs and outputs today. This is for two main
reasons:
● time preference for money
● interest
8. One major advantage of renewable technologies is that the fuel is free.