Page 211 - Fundamentals of Physical Volcanology
P. 211
9780632054435_4_012.qxd 12/10/2007 12:33PM Page 188
188 CHAPTER 12
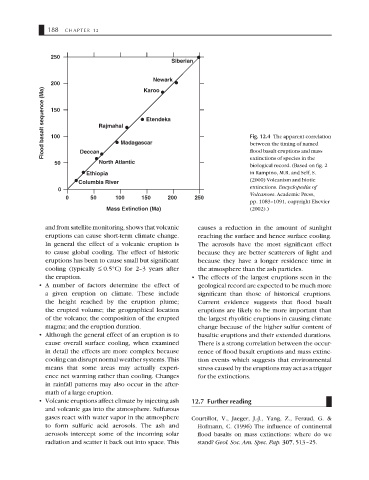
250
Siberian
Newark
200 Karoo
Flood basalt sequence (Ma) 150 Rajmahal Madagascar Fig. 12.4 The apparent correlation
Etendeka
100
flood basalt eruptions and mass
extinctions of species in the
50 Deccan North Atlantic between the timing of named
biological record. (Based on fig. 2
Ethiopia in Rampino, M.R. and Self, S.
(2000) Volcanism and biotic
Columbia River
extinctions. Encyclopedia of
0
Volcanoes. Academic Press,
0 50 100 150 200 250
pp. 1083–1091, copyright Elsevier
Mass Extinction (Ma) (2002).)
and from satellite monitoring, shows that volcanic causes a reduction in the amount of sunlight
eruptions can cause short-term climate change. reaching the surface and hence surface cooling.
In general the effect of a volcanic eruption is The aerosols have the most significant effect
to cause global cooling. The effect of historic because they are better scatterers of light and
eruptions has been to cause small but significant because they have a longer residence time in
cooling (typically ≤ 0.5°C) for 2–3 years after the atmosphere than the ash particles.
the eruption. • The effects of the largest eruptions seen in the
• A number of factors determine the effect of geological record are expected to be much more
a given eruption on climate. These include significant than those of historical eruptions.
the height reached by the eruption plume; Current evidence suggests that flood basalt
the erupted volume; the geographical location eruptions are likely to be more important than
of the volcano; the composition of the erupted the largest rhyolitic eruptions in causing climate
magma; and the eruption duration. change because of the higher sulfur content of
• Although the general effect of an eruption is to basaltic eruptions and their extended durations.
cause overall surface cooling, when examined There is a strong correlation between the occur-
in detail the effects are more complex because rence of flood basalt eruptions and mass extinc-
cooling can disrupt normal weather systems. This tion events which suggests that environmental
means that some areas may actually experi- stress caused by the eruptions may act as a trigger
ence net warming rather than cooling. Changes for the extinctions.
in rainfall patterns may also occur in the after-
math of a large eruption.
• Volcanic eruptions affect climate by injecting ash 12.7 Further reading
and volcanic gas into the atmosphere. Sulfurous
gases react with water vapor in the atmosphere Courtillot, V., Jaeger, J.-J., Yang, Z., Feraud, G. &
to form sulfuric acid aerosols. The ash and Hofmann, C. (1996) The influence of continental
aerosols intercept some of the incoming solar flood basalts on mass extinctions: where do we
radiation and scatter it back out into space. This stand? Geol. Soc. Am. Spec. Pap. 307, 513–25.