Page 44 - Fundamentals of Physical Volcanology
P. 44
9780632054435_4_002.qxd 12/10/2007 12:18PM Page 21
MAGMA GENERATION AND SEGREGATION 21
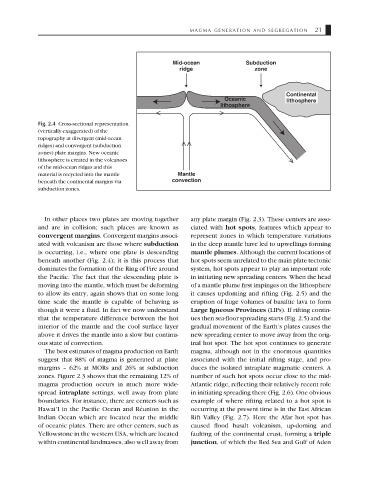
Mid-ocean Subduction
ridge zone
Continental
Oceanic lithosphere
lithosphere
Fig. 2.4 Cross-sectional representation
(vertically exaggerated) of the
topography at divergent (mid-ocean
ridges) and convergent (subduction
zones) plate margins. New oceanic
lithosphere is created in the volcanoes
of the mid-ocean ridges and this
material is recycled into the mantle Mantle
beneath the continental margins via convection
subduction zones.
In other places two plates are moving together any plate margin (Fig. 2.3). These centers are asso-
and are in collision; such places are known as ciated with hot spots, features which appear to
convergent margins. Convergent margins associ- represent zones in which temperature variations
ated with volcanism are those where subduction in the deep mantle have led to upwellings forming
is occurring, i.e., where one plate is descending mantle plumes. Although the current locations of
beneath another (Fig. 2.4); it is this process that hot spots seem unrelated to the main plate tectonic
dominates the formation of the Ring of Fire around system, hot spots appear to play an important role
the Pacific. The fact that the descending plate is in initiating new spreading centers. When the head
moving into the mantle, which must be deforming of a mantle plume first impinges on the lithosphere
to allow its entry, again shows that on some long it causes updoming and rifting (Fig. 2.5) and the
time scale the mantle is capable of behaving as eruption of huge volumes of basaltic lava to form
though it were a fluid. In fact we now understand Large Igneous Provinces (LIPs). If rifting contin-
that the temperature difference between the hot ues then sea-floor spreading starts (Fig. 2.5) and the
interior of the mantle and the cool surface layer gradual movement of the Earth’s plates causes the
above it drives the mantle into a slow but continu- new spreading center to move away from the orig-
ous state of convection. inal hot spot. The hot spot continues to generate
The best estimates of magma production on Earth magma, although not in the enormous quantities
suggest that 88% of magma is generated at plate associated with the initial rifting stage, and pro-
margins – 62% at MORs and 26% at subduction duces the isolated intraplate magmatic centers. A
zones. Figure 2.3 shows that the remaining 12% of number of such hot spots occur close to the mid-
magma production occurs in much more wide- Atlantic ridge, reflecting their relatively recent role
spread intraplate settings, well away from plate in initiating spreading there (Fig. 2.6). One obvious
boundaries. For instance, there are centers such as example of where rifting related to a hot spot is
Hawai’I in the Pacific Ocean and Réunion in the occurring at the present time is in the East African
Indian Ocean which are located near the middle Rift Valley (Fig. 2.7). Here the Afar hot spot has
of oceanic plates. There are other centers, such as caused flood basalt volcanism, up-doming and
Yellowstone in the western USA, which are located faulting of the continental crust, forming a triple
within continental landmasses, also well away from junction, of which the Red Sea and Gulf of Aden