Page 234 - Fundamentals of Radar Signal Processing
P. 234
received signal contains echoes from multiple targets at different ranges?
Start by choosing T = τ, the minimum value that results in a causal
M
matched filter. Now suppose the input to the matched filter is the echo from a
target at an unknown range R , corresponding to a time delay t = 2R /c. The
0
0
0
signal component of the output of the matched filter will be
(4.22)
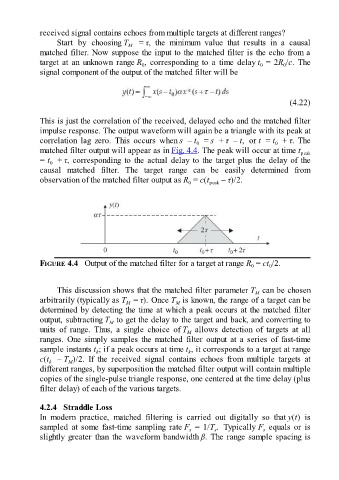
This is just the correlation of the received, delayed echo and the matched filter
impulse response. The output waveform will again be a triangle with its peak at
correlation lag zero. This occurs when s – t = s + τ – t, or t = t + τ. The
0
0
matched filter output will appear as in Fig. 4.4. The peak will occur at time t peak
= t + τ, corresponding to the actual delay to the target plus the delay of the
0
causal matched filter. The target range can be easily determined from
observation of the matched filter output as R = c(t peak – τ)/2.
0
FIGURE 4.4 Output of the matched filter for a target at range R = ct /2.
0
0
This discussion shows that the matched filter parameter T can be chosen
M
arbitrarily (typically as T = τ). Once T is known, the range of a target can be
M
M
determined by detecting the time at which a peak occurs at the matched filter
output, subtracting T to get the delay to the target and back, and converting to
M
units of range. Thus, a single choice of T allows detection of targets at all
M
ranges. One simply samples the matched filter output at a series of fast-time
sample instants t ; if a peak occurs at time t , it corresponds to a target at range
k
k
c(t – T )/2. If the received signal contains echoes from multiple targets at
k
M
different ranges, by superposition the matched filter output will contain multiple
copies of the single-pulse triangle response, one centered at the time delay (plus
filter delay) of each of the various targets.
4.2.4 Straddle Loss
In modern practice, matched filtering is carried out digitally so that y(t) is
sampled at some fast-time sampling rate F = 1/T . Typically F equals or is
s
s
s
slightly greater than the waveform bandwidth β. The range sample spacing is