Page 328 - Fundamentals of Radar Signal Processing
P. 328
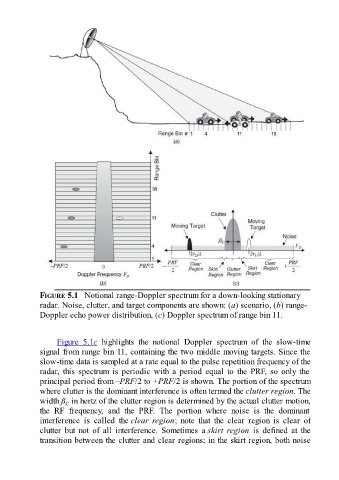
FIGURE 5.1 Notional range-Doppler spectrum for a down-looking stationary
radar. Noise, clutter, and target components are shown: (a) scenario, (b) range-
Doppler echo power distribution, (c) Doppler spectrum of range bin 11.
Figure 5.1c highlights the notional Doppler spectrum of the slow-time
signal from range bin 11, containing the two middle moving targets. Since the
slow-time data is sampled at a rate equal to the pulse repetition frequency of the
radar, this spectrum is periodic with a period equal to the PRF, so only the
principal period from –PRF/2 to +PRF/2 is shown. The portion of the spectrum
where clutter is the dominant interference is often termed the clutter region. The
width ß in hertz of the clutter region is determined by the actual clutter motion,
C
the RF frequency, and the PRF. The portion where noise is the dominant
interference is called the clear region; note that the clear region is clear of
clutter but not of all interference. Sometimes a skirt region is defined at the
transition between the clutter and clear regions; in the skirt region, both noise