Page 316 - Fundamentals of Reservoir Engineering
P. 316
REAL GAS FLOW: GAS WELL TESTING 251
8.5 COMPARISON OF THE PRESSURE SQUARED AND PSEUDO PRESSURE
SOLUTION TECHNIQUES
2
Much has been written 3,4,5 about the conditions under which the p and m(p) solution
techniques give identical results. Comparison of the methods can best be summarised
by directly comparing equ. (8.5) and equ. (8.15) i.e.
2 p
p − p 2 pdp
when is wf equivalent to () − mp wf ) = 2
mp
(
µΖ p wf µΖ
( pp+ wf ) ( p p− wf ) p pdp
or equivalent to (8.17)
2 µΖ p wf µΖ
where both µ and Z appearing on the left hand side are evaluated at (p p )/ 2+ wf . As
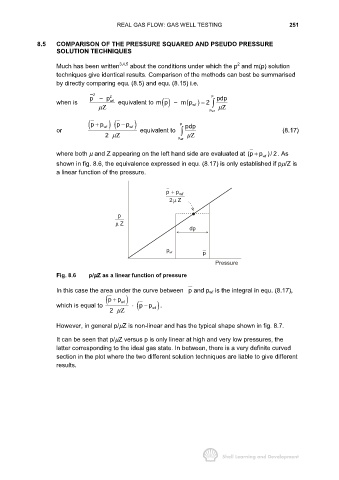
shown in fig. 8.6, the equivalence expressed in equ. (8.17) is only established if pµ/Z is
a linear function of the pressure.
p + p wf
2Z
µ
p
µ Z
dp
p wf p
Pressure
Fig. 8.6 p/µZ as a linear function of pressure
In this case the area under the curve between p and p wf is the integral in equ. (8.17),
( pp+ wf )
which is equal to ⋅ ( pp wf ) .
−
2 µΖ
However, in general p/µZ is non-linear and has the typical shape shown in fig. 8.7.
It can be seen that p/µZ versus p is only linear at high and very low pressures, the
latter corresponding to the ideal gas state. In between, there is a very definite curved
section in the plot where the two different solution techniques are liable to give different
results.