Page 79 - Fundamentals of Reservoir Engineering
P. 79
SOME BASIC CONCEPTS IN RESERVOIR ENGINEERING 18
700
PSEUDO CRITICAL PRESSURE, psia 650
600
CONDENSATE WELL FLUID
550 MISCELLANEOUS GASES
PSEUDO CRITICAL TEMPERATURE, degrees Rankine 500
450
400
350
300
0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1.0 1.1 1.2
GAS GRAVITY (Air = 1)
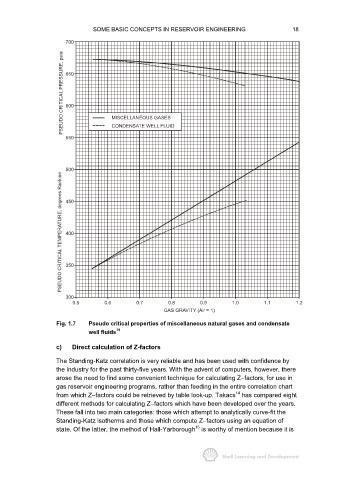
Fig. 1.7 Pseudo critical properties of miscellaneous natural gases and condensate
well fluids 19
c) Direct calculation of Z-factors
The Standing-Katz correlation is very reliable and has been used with confidence by
the industry for the past thirty-five years. With the advent of computers, however, there
arose the need to find some convenient technique for calculating Z−factors, for use in
gas reservoir engineering programs, rather than feeding in the entire correlation chart
14
from which Z−factors could be retrieved by table look-up. Takacs has compared eight
different methods for calculating Z−factors which have been developed over the years.
These fall into two main categories: those which attempt to analytically curve-fit the
Standing-Katz isotherms and those which compute Z−factors using an equation of
15
state. Of the latter, the method of Hall-Yarborough is worthy of mention because it is