Page 109 - Gas Purification 5E
P. 109
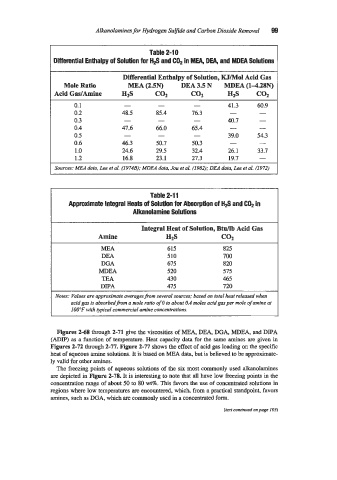
Alkanolamines for Hydrogen Sulfide and Carbon Dioxide Removal 99
Table 2-1 0
Differential Enthalpy of Solution for tl# and C02 in MEA, DEA, and MDEA Solutions
Differential Enthalpy of Solution, KJ/Mol Acid Gas
Mole Ratio MEA (2.5N) DEA 3.5 N MDEA (1428N)
Acid GadAmine H2S co2 COZ HIS cot
0.1 - - - 41.3 60.9
0.2 48.5 85.4 76.3 - -
0.3 - - - 40.7 -
0.4 47.6 66.0 65.4 - -
0.5 - - - 39.0 54.3
0.6 46.3 50.7 50.3 - -
1 .o 24.6 29.5 32.4 26.1 33.7
1.2 16.8 23.1 27.3 19.7 -
Sources: MEA data, Lee et al. (I974B); MDE4 data, Jou et al. (1982); DEA data, Lee et al. 11972)
Table 2-11
Approximate Integral Heats of Solution for Absorption of Hfi and C02 in
Alkanolamine Solutions
Integral Heat of Solution, Btdb Acid Gas
Amine H2S co2
MEA 615 825
DEA 510 700
DGA 675 820
MDEA 520 575
TEA 430 465
DIPA 475 720
Notes: Values are approximate averagesfrorn several sowces; based on total heat released when
acid gas is absorbedj-om a mole ratio of 0 to about 0.4 moles acid gas per mole of amine at
100°F with typical commercial amine concentrations.
Figures 2-68 through 2-71 give the viscosities of MEA, DEA, DGA, MDEA, and DIPA
(ADP) as a function of temperature. Heat capacity data for the same amines are given in
Figures 2-72 through 2-77. Figure 2-77 shows the effect of acid gas loading OI? the specific
heat of aqueous amine solutions. It is based on MEA data, but is believed to be approximate-
ly valid for other amines.
The freezing points of aqueous solutions of the six most commonly used ahnolamines
are depicted in Figure 2-78. It is interesting to note that all have low freezing points in the
concentration range of about 50 to 80 wt%. This favors the use of concentrated solutions in
regions where low temperatures are encountered, which, from a practical standpoint, favors
amines, such as DGA, which are commonly used in a concentrated form.
(rat conrinued on page I03j