Page 108 - Gas Purification 5E
P. 108
98 Gas PuriJication
30wtK MDEA I
90 I 1
0 30wtKMEA
20wt%MEA+lOwt%MDEA
80 0 10 wt% MEA + 10 wt% MDEA
v 3.0 wt% MEA + 27 wt% MDEA
U 1.5wt% MEA+28.5wt% MDEA
70
60
+
0
50
40
30
I
0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2 1.4
a cop (mol of C02/mol of amine)
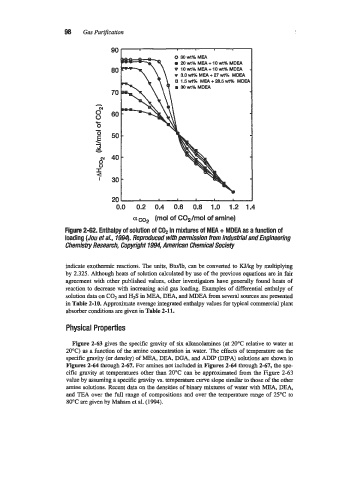
Figure 2-62. Enthalpy of solution of CO, in mixtures of MEA + MDEA as a function of
loading (Jou et a/., 1994). Reproduced with pemjssion from Indudrial and Engineering
Chemistry Research, Copyright 1994, American Chemical Sociefy
indicate exothermic reactions. The units, Btdlb, can be converted to Wkg by multiplying
by 2.325. Although heats of solution calculated by use of the previous equations are in fair
agreement with other published values, other investigators have generally found heats of
reaction to decrease with increasing acid gas loading. Examples of differential enthalpy of
solution data on C02 and H2S in MEA, DEA, and MDEA from several sources are presented
in Table 2-10. Approximate average integrated enthalpy values for typical commercial plant
absorber conditions are given in Table 2-11.
Physical Properties
Figure 2-63 gives the specific gravity of six allcanolamines (at 20°C relative to water at
ZOOC) as a function of the amine concentration in water. The effects of temperature on the
specific gravity (or density) of MEA, DEA, DGA, and ADP (DPA) solutions are shown in
Figures 2-64 through 2-67. For amines not included in Figures 2-64 through 2-67, the spe-
cific gravity at temperatures other than 20°C can be approximated from the Figure 2-63
value by assuming a specific gravity vs. temperature curve slope similar to those of the other
amine solutions. Recent data on the densities of binary mixtures of water with MEA, DEA,
and TEA over the full range of compositions and over the temperature range of 25°C to
80°C are given by Maham et al. (1994).